At any time of year, lightning strikes can occur, frequently passing fast and leaving minor damage in their wake. In the UK, summertime thunderstorms are most likely to deliver colossal hail, windy gusts and deluges of rain that can disrupt transport systems and inflict property damage.
Given their detrimental effects on our lives and jobs, we must learn more about lightning strikes and take the necessary preventive measures in advance. Let's now study different facts and precautions against lightning strikes in the UK.
Furthermore, some lightning strikes can cause power surges or cuts, so it is essential to have a Jackery Solar Generator to charge appliances in an emergency. You can even take it inside your home because it doesn't make any noise or give off any pollution.
|
Key Takeaways: |
|
l This article provides detailed data and facts about lightning strikes in the UK, helping you gain a preliminary understanding of the historical and current situation. l The UK, Ireland, and the surrounding waters usually see between 200,000 and 300,000 lightning strikes annually. l There was a one in 33 million chance of being struck and murdered on average each year. The risk was one person in 71 million if only the last ten years were considered, with fewer lightning deaths. l We have detailed some safety measures and tips for a lightning strike. l Lightning strikes usually cause power outages, so we recommend Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus and 2000 Plus for emergencies. |
Lightning Strikes in The UK
There are a lot of hazards associated with lightning, a high-voltage, brief natural electrical discharge that can occur inside clouds or between clouds and the ground. It would help if you moved indoors when thunder roars since doing so can significantly lower your chance of being struck by lightning.
Because lightning usually strikes the highest item in the area, large, concrete buildings with walls and floors are safer than solitary trees or open areas. Just 25% of the lightning produced by thunderstorms is potentially hazardous cloud-to-ground strikes.
Most other lightning strikes occur entirely inside clouds and are only apparent as a cloud brightening, sometimes called "sheet lightning."
The UK, Ireland, and the surrounding waters usually see between 200,000 and 300,000 lightning strikes annually. A 'thunderstorm day' could see up to 10,000 strikes, but on evil days, there could be over 50,000, as on June 28, 2012, when there were 64,000.
The UK Met Office offers helpful information that describes the formation of thunderstorms, lightning, and thunder.
Although they can happen anywhere in the UK, thunderstorms are most common in southeast England during the summer months of May through August. Lightning, however, occurs during any month of the year. While there is a considerable amount of annual variation in the frequency of thunderstorms, the map below illustrates the total number of thunderstorms over 40 years from 1971 to 2010

Principal data sources include TORRO and TCO Thunderstorm observers' reports, Data from the Climatological Observers Link station (provided by Roger Brugge) and the Met Office's Monthly Weather Report (available until 1993).
Data has been compared between neighbouring stations to ensure consistency. Still, it should be noted that less populated locations will have means based on fewer observations available. Under-recording is likely because thunder observation necessitates keeping a "24-hour watch" on the weather.
Data of Lightning Strikes in The UK
Between 1987 and 2016, there were 58 confirmed lightning deaths in the UK or two fatalities per year. There was a one in 33 million chance of being struck and murdered on average each year. The risk was one person in 71 million if only the last ten years were considered, with fewer lightning deaths.
Compared to one person every two million years a century ago, the chance of dying from lightning strikes has significantly decreased. Depending on what you're doing at the time, there are different risks of being killed by lightning in the UK.
Based on the pertinent analysis, they categorise activities into three main categories. Work-related activities accounted for 15% of all deaths between 1987 and 2016, everyday activities accounted for 13%, and outdoor leisure, recreation, and sports pursuits accounted for 72%.
Approximately half of all deaths related to leisure, recreation, and sports activity were caused by leisure strolling on hills, mountains, cliff-tops, and outdoor sports like cricket, fishing, football, golf, rugby, and watersports. The age group of 20 to 29 years old saw the most significant number of deaths.
Sundays accounted for 26% of all fatalities, indicating that a lot of people engage in higher-risk recreational activities on this day. 80% of all deaths occurred in the four months from May to August.
(Data Source: LIGHTNING DEATHS IN THE UK: A 30-YEAR ANALYSIS OF THE FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO PEOPLE BEING STRUCK AND KILLED -BY DEREK M. ELSOM AND JONATHAN D.C. WEBB)
Chance of Getting Struck by Lightning
There are around 300,000 lightning strikes in the UK annually. Of these hits, 30 to 60 persons are killed on average, and three (5-10%) of these are caused by lightning. According to UK mortality figures, two people died from lightning strikes in 2005.
According to ROSPA, the most vulnerable are those who spend much time outside, such as hill walkers, climbers, golfers, and agricultural labourers. Based on an estimated 67,081,000 people living in the UK, if 60 persons are struck annually, that translates to one person for every 1,118,016 people (Data Source: Office for National Statistics).
Other sources, however, indicate a range of disparate chances. Some give more comforting odds of 10,000,000 to one, while others say you have a 300,000 to one chance of being struck. In any case, the likelihood of being struck by lightning is significantly higher than that of winning the big prize in the National Lottery.
In addition, you may determine your distance from a thunderstorm. You can finish it by keeping track of the number of seconds between the sound of thunder and lightning, which is always visible first.
Lightning and thunder are created simultaneously during a storm, but since light travels quicker than sound, you will see the strike or flash before hearing the deep rumble or clap. We hear a rumbling thunderclap due to the air's quick expansion into the cooler air surrounding it due to this intense heating.
On the other hand, you could not even hear any thunder at all if the storm was far away. To prevent getting caught in the storm, it is ideal to conduct any counting indoors.

What Happens If You Are Struck by Lightning?
Most of the time, a lightning strike does not result in death. Merely 5% to 10% of individuals die at the scene. Even though lightning is five times hotter than the sun's surface, it doesn't produce significant burns under normal conditions, but it can induce brain damage and interfere with heart rhythm.
You should call for emergency medical assistance as soon as you witness someone struck by lightning. Most of the time, they'll be dazed; if not, try to calm them down. Assure them and strike up a discussion if they can. Finding out their identity and any significant medical conditions will be helpful to the emergency services, but don't push too hard - what matters most is that they remain calm.
The initial hours following a lightning strike are the riskiest, although receiving quality medical attention is crucial. Some patients with heart problems require continuous care. It's normal to experience some memory loss and focus issues due to COVID-19—the kind of "brain fog" many of us are familiar with today.
Although it is uncommon, persistent discomfort does occur; headaches are the most common ailment, and many patients have pins and needles. Sensations may be impacted. Things may taste or smell different, and hearing may become more acute.
Not surprisingly, PTSD is common among lightning-hit survivors, and despair can also set in. Friends and family must understand that these are long-term impacts and that the survivor will require assistance. Lightning Strike & Electrical Shock Survivors International is a global peer support group that can assist with this.
Not only that, but survivors often have ornate, branching scars that show the path lightning takes through their bodies. These are rarely uncomfortable, and many find them to be lovely. They designate survivors of lightning strikes as unique.
Lightning Strikes Safety Measures & Tips
It may not always be straightforward to locate the appropriate shelter when lightning strikes. If you are stranded outdoors during a storm, the following are the most effective strategies. Knowing how to keep safe during lightning strikes in the UK is essential if you find yourself in an affected area.

Before The Thunderstorm
- If you don't already have a surge protector, disconnect any non-essential items, as lightning can result in power surges.
- Seek refuge, if at all possible. As lightning can strike up to 10 miles from a storm's centre, you can already tell where the next ground flash may occur when you hear thunder.
During The Thunderstorm
- Please avoid using the landline unless it's an emergency because telephone wires can potentially carry electricity.
- If you're outside, stay away from the water and locate a low-lying area free of obstructions like trees, poles, or metal objects.
- Avoid playing sports like boating on a lake, golf, or rod fishing.
- Look for metal objects such as golf clubs, motorbikes, bicycles, wheelchairs, mobility scooters, and rails that can potentially conduct or attract lightning. Try to avoid the metal poles if you are in a tent.
- It could be wise to crouch low to the ground in an open area, place your hands on your knees, and tuck your head between them. Avoid touching the earth with your body as much as possible; avoid lying down on it.
- When you notice your hair tense, instantly adjust to the posture above.
After The Thunderstorm
- Steer clear of damaged wires or dead electrical lines.
- Those struck by lightning frequently sustain severe burns. Make sure they have a pulse; the impact also affects the heart.
- Stay inside your car and roll down the windows if you happen to be caught in a lightning or thunderstorm. This is because, in most vehicles with a metal roof and frame, the frame will serve as a conductive Faraday cage, allowing current to flow around the occupants and out to the ground.
- Soft-top convertibles are particularly vulnerable to lightning strikes because of their fabric roofs.
- Be advised that many modern cars include other components, such as radios and GPS, through which current may pass. Vehicles with metal foot pedals, steering wheels, and interior handles can also carry current.
- Lightning strikes can potentially cause external and interior damage to cars.
- Those most vulnerable to sudden gusts of wind are motorcyclists, cyclists, and drivers of high-sided vehicles. Thunderstorms can also bring this risk.
- Remember to provide more space than usual for vulnerable road users, including pedestrians, bike riders, and motorcyclists. Since side breezes are more likely to blow them about, you should always keep a safe distance from them.
- Reduce your speed to minimise the distance you cover when the wind blows you about.
- Driving during hail storms can be exceedingly hazardous as it can impair your visibility and cause harm to your car. If there is a lot of hail, stop, find a safe spot to pull over, and stay in the car.
- Also, if you are in a thunderstorm, you should take many safety steps. During a storm, safety precautions must always be taken indoors and outside.
Safety Measures Indoors
Even if you're safer inside, statistics indicate that one-third of lightning-related injuries happen indoors, so you're not entirely secure. Avoiding water contact during a thunderstorm is one way to take extra safety precautions because lightning can pass through plumbing systems.

Avoid using electronic devices in your house since lightning strikes can swiftly pass through corded phones, radios, televisions, and other electrical systems. It would help if you stayed away from the doors and windows. Even though lightning strikes are uncommon, there's always a chance they could occur. You must take some easy steps to reduce the risk to your safety.
Lightning strikes may cause a power surge, and your house will have no electricity. Preparing for an emergency generator, like Jackery Solar Generator, is crucial to ensure no further damage due to power outages. It doesn't produce any emissions and is safe to use indoors.
Outdoor Precautions
If you're outside, you should seek cover when you notice a flash of lightning. If lightning is predicted, postpone your journey or any outdoor activities. Always remember the 30-30 rule in an unexpected situation.
Count to thirty when you notice the lightning. If you hear thunder before you count thirty, get inside as soon as possible. Wait half an hour after the last thunderclap before venturing outside again. Even if you are more than 100 feet away from the lightning strike, electric currents can still run along the ground and kill you if you are stranded outside and unable to locate safe shelter.
To avoid this, squat low and make sure only your feet touch the ground. Always remember that lightning can pass quickly through wires or metal bars embedded in concrete floors or walls, so avoid these types of buildings.
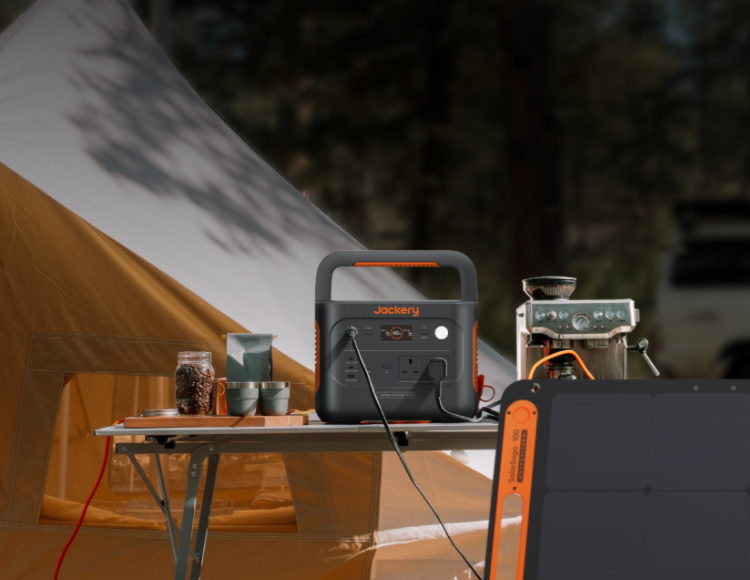
Jackery Solar Generators for Emergencies
The Jackery Solar Generator can be a backup power source if an emergency happens, making life much easier when you don't have control.
When there is a power surge, storm, or more emergencies, the Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus and Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus will keep you and your family running. Both comprise SolarSaga solar panels and Portable Power Stations from the Explorer series.

The Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus has an expandable capacity from 1264Wh to 5 kWh to power some household appliances. The most important thing is that it has emergency supercharging within an hour in an emergency.
Besides, the Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus has a battery that can be expanded from 2 kWh to 12 kWh. For this reason, the Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus and 2000 Plus are better choices for emergencies at home.
Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus
The Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus is also the best portable power supply for your home. It combines Jackery Explorer 1000 Plus with SolarSaga 100W solar panels to use solar energy effectively.
Featuring a 2000W full-power pure sine wave inverter and a stunning 1264Wh long-lasting LiFePO4 battery, the Explorer 1000 Plus offers abundant energy for almost all essential devices. Remarkably, it can increase its capacity to 5 kWh by incorporating up to 3 additional battery packs.
A wall charge from 0% to 100% of the battery requires 100 minutes, while solar charging with four SolarSaga 200W panels takes 2 hours. Additionally, the innovative ChargeShield technology and consistent power delivery avoid equipment damage.

Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus
Jackery has unveiled the Solar Generator 2000 Plus, a cutting-edge portable power solution with exceptional performance. Thanks to its substantial capacity and formidable power output, this device can sustain the operation of standard domestic appliances for several weeks and fulfil all the power needs associated with emergency or professional activity.
The Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus allows adding extra battery packs, which boosts the capacity from 2 kWh to a remarkable 12 kWh, thus enhancing the solar charging capabilities significantly. With the ability to be expanded to 3000W, this solar product offers a 30% higher rated power than other 2 kWh solar goods available in the market.
The Explorer 2000 Plus is an industry's pioneering add-on battery pack that can be recharged using solar panels. This feature enhances versatility, improves charging efficiency, and reduces charging time. The LiFePO4 battery, with its sophisticated technology, guarantees a lifespan of 10 years, even with daily usage limited to once per day.

Tips for using a generator during an emergency
Generally, most people use backup power to keep themselves going during an emergency. Consider combining basic or complex power generation options to make your home resilient to power cuts. You can then use backup power for lighting, food preservation, cooling, heating, preventing mould, etc.
But follow these safety tips when using a generator at home during an emergency:
- Operate the generator only on dry surfaces and with dry hands to keep it dry. Do not use the generator outdoors in wet or rainy conditions.
- Check the generator's wires for cuts or tears before use.
- Regularly inspect and maintain your generator. Consider signing a maintenance contract to provide service at least once a year.
- Start the generator regularly, even when no power is cut, to ensure it functions properly.
Lightning Strikes in The UK FAQs
The following are the frequently asked questions about the lightning strikes in the UK:
- Is it safe to drive in a thunderstorm?
Diving during a thunderstorm is typically commended, but life is an emergency because the conditions are usually deplorable. It is preferable to find a safe place to park off the highway during thunder and lightning, close your windows, and stay inside if you are already on the road.
An automobile with a soft top, sometimes called a convertible, is less safe than a hard top because lightning could ignite the fabric roof. It is essential to find nearby cover if you are driving. When driving, there are other hazards besides lightning. Rain and strong winds are expected during thunderstorms, which makes driving hazardous.
- Can you use an umbrella in lightning?
No, it's advisable not to use an umbrella. You risk getting hurt using an umbrella during a thunderstorm since metal things conduct lightning. The same applies to other metal items you could come across outside, such as bicycles, golf clubs, buggies, fishing rods, pushchairs, and strollers. Moving as far away as possible from metal railings and fencing is also advised.
- Should you turn off electrical appliances in the house?
Indeed, to shield non-essential equipment from power surge damage during a thunderstorm, you should turn them off and disconnect them. That goes for any electrical gadget that is plugged in, as well as the Internet.
Watching TV after the storm has passed will be safe, but you may still use a tablet or laptop as long as they're not plugged into the primary power source. Mobile phones are secure, but landline telephones that plug into the wall should also be avoided.
- Is it safe to watch a thunderstorm from a window?
No, and for some folks, that's probably bad news. Although many people like to watch thunderstorms pass over, they can be dangerous inside your house. Avoid leaning on external walls during a storm since lightning can pass through concrete in walls, flooring, and metal cables and bars. There's also a chance that oversized items, like trees, will be blown into your building during strong gusts. Just in case, it's advisable to avoid windows and doors.
Final Thoughts
Given that there are about 300,000 lightning strikes in the UK annually, it is crucial to comprehend and put lightning strike safety procedures into practice. We think that by taking preemptive measures now, you can avert the catastrophic effects of tomorrow's storm.