Electricity consumption is essential in assessing energy use and household living costs in the UK. Recently, measures to improve energy efficiency have steadily reduced household electricity consumption.
But do you know how much electricity the average household uses per day? Specifically, how much kilowatt-hours (kWh) does the average household consume daily? Knowing the kWh consumption of the average UK household can provide insight into energy efficiency measures and the environmental impact.
This guide will demonstrate questions like "How many kWh does a house use in the UK?". Besides, we highly recommend Jackery Solar Generator, a portable solar power solution, to charge your appliances and save on electricity bills.
|
Key Takeaways: |
|
Before you know how many kilowatt-hours your home consumes, it's essential to understand the kilowatt-hour (kWh) equation. The average UK household (a typical UK household with 2 to 3 occupants) uses about 2,900 kWh of electricity annually and 242 kWh per month. Several electronic devices and appliances consume many of a home's kilowatt-hours. Kitchen appliances (including fridges, freezers, hobs, ovens, kettles, microwaves, etc.) account for around 17% of the average household's electricity bill. In contrast, the bathroom appliances consume about 16% of electricity. We highly recommend Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus, 1000 Plus, and 500 to save your electric bills with solar energy. |
Understand kWh and Electricity Consumption
Before you know how many kilowatt-hours your home consumes, it's essential to understand what kilowatt-hours (kWh) mean and how they relate to electricity consumption.
What Is A Kilowatt-Hour?
A kilowatt-hour (kWh) is the product of power (in kilowatts) multiplied by the time (in hours) it's consumed. In simple terms, a kWh represents 1,000 watts used in one hour.
Here's an example to help you understand kilowatt-hours better.
A 100-watt light bulb must be on for 10 hours to consume 1 kWh of electricity. So, if a 1,000-watt refrigerator runs for one hour, it will consume 1 kWh of electricity.
How Do Kilowatt-Hours Relate To Electricity Consumption?
In simple terms, kilowatt-hours measure the electricity consumed over a certain period. For home electricity use, kilowatt-hours are a valuable measure of how much electricity a house consumes monthly or yearly. Electricity suppliers often calculate your electricity usage in kilowatt-hours and charge customers accordingly. (Typically, homes served by electricity suppliers are equipped with a meter that records electricity consumption.) In addition, homeowners can understand their electricity consumption habits by understanding average electricity consumption. For this reason, kilowatt-hours (1,000 watts per hour) are more commonly used to calculate household electricity usage.
However, kilowatt-hours are not limited to residential homes; industries, businesses, and even entire countries rely on kilowatt-hours to measure and manage their electricity consumption. All electricity sectors can optimise power efficiency, reduce costs, and minimise environmental impact by gaining insight into kilowatt-hours.
How Many kWh Does A House Use in The UK?
Typically, electricity suppliers use kilowatt-hours to understand how much electricity you use and calculate your electricity bill.
According to sources such as Ofgem and OVO Energy, the average UK household (a typical UK household with 2 to 3 occupants on average) uses about 2,900 kWh of electricity annually. So, how much does a typical UK household consume per month? 242 kWh.
Here is the average daily electricity usage of households currently published by the three UK government departments:
|
Government Department |
Average Daily Use |
Average Annual Use |
|
Ofgem |
7.9 kWh |
2,900 kWh |
|
Department for Energy Security & Net Zero |
9.9 kWh |
3,600 kWh |
|
BEIS |
8.5 kWh |
3,100 kWh |
Note*: These data may change since some houses become more energy-efficient or choose renewable energy.
(Data Source: aquaswitch)
Different Profiles
However, the average electricity usage defined by the electricity profile categories varies widely.
Electricity Profile Class 1 (Domestic Unrestricted)
Most homes fall into this category and typically have low usage. Most home-run businesses also fall into this category and do not usually need to switch to a business energy plan.
Electricity Profile Class 2 (Domestic Economy 7)
These homes have an Economy 7 meter ("time-of-use") installed to help small energy users save money during peak and off-peak times.
|
Electricity Profile Class 1 |
|
|
Consumption Rate |
Usage (in kWh) |
|
Low |
1,800 |
|
Medium |
2,900 |
|
High |
4,200 |
|
Electricity Profile Class 2 |
|
|
Consumption Rate |
Usage (in kWh) |
|
Low |
2,400 |
|
Medium |
4,100 |
|
High |
7,000 |
(Data Source: UK Power)
From the data above, we can get that the low electricity consumption in different power profile categories is 1,800kWh to 2,400kWh, the medium consumption is 2,900kWh to 4,200kWh, and the high consumption is between 4,100kWh and 7,000kWh. From this, we can also get the annual average consumption of 2,900kWh.
So, how many kWh does a typical British household consume per day?
However, it is not easy to calculate daily electricity consumption accurately because each household's electricity consumption varies greatly depending on factors such as the number of people living in it, the type of appliances used, and the house's energy efficiency. Based on the above content and data, the average household's electricity consumption is about 8kWh (estimated value).
Different Regions
Power consumption in the UK differs by region, with the highest levels observed in the East, South East, and South West of England.
The East, South East, and South West regions exhibit the highest consumption levels, averaging over 3,600 kilowatt-hours per household.
The North East region exhibits the lowest average home electricity usage per metre, constantly remaining approximately 13 to 15 per cent below the average for Great Britain.
- The median power consumption in Outer London is 5,161 kWh.
- The power consumption in Scotland amounts to 3,374.3 kilowatt-hours.
- The electricity consumption in the East Midlands is 3,338.7 kilowatt-hours.
- The electricity consumption in the West Midlands is 3,327.3 kilowatt-hours.
The typical yearly electricity consumption per family in the UK ranges from roughly 2,900 kWh to 3,731 kWh.

(Data Source: Statista)
How Do You Calculate kWh Power Consumption?
You can estimate your home's electricity use manually. Calculating average kWh consumption can help you understand usage patterns, reduce electricity consumption, and manage your bills.
To manually calculate your electricity usage, follow these steps:
Step 1: Collect your electricity bill.
Collect your monthly or quarterly electricity bills, showing the total kWh used.
Step 2: Estimate kWh power consumption.
If you have a monthly electricity bill, add the kWh for 12 months and divide by 12 to get your monthly average kWh. If you have a quarterly electricity bill, add the kWh for four quarters and divide by 4 to get your quarterly average kWh. Similarly, you can use the annual average kWh, the monthly average kWh, and the quarterly average kWh to get your daily kWh.
How do you estimate the electricity consumption of my appliances?
Estimating the electricity consumption of my appliances is very simple. All you need to know is the appliance's wattage and use length.
The appliance wattage * number of hours per day / 1,000 = kWh used. For example, a 200-watt light bulb used 5 hours daily consumes 1 kWh/day.
Factors Affect kWh A House Use in The UK
Household size, lifestyle, and weather conditions can affect electricity consumption. Additionally, gaining insight into the factors that affect a home's electricity usage can help individuals and households make informed decisions about electricity usage and find ways to reduce it.

- Household Size
The more family members there are, the more appliances are used simultaneously, resulting in higher kilowatt-hour consumption. Therefore, a household with a larger population generally uses more electricity than a smaller one.
One key factor that affects a household's kilowatt-hour consumption is the size of the house. Each house has a different number of rooms and heating and lighting requirements. Generally, larger houses require more electricity to heat and power them.
A small house or apartment usually has fewer people, so less electricity is needed to heat, calm, and power appliances.
A medium-sized house can accommodate a moderate number of occupants and may have more appliances and equipment, so electricity consumption is slightly higher.
Larger homes usually have more people living in them and require more electricity for heating, cooling, and powering various appliances and electronic devices.
|
Type of Home |
Size of Home |
Average Annual Electricity Usage |
|
Small Home |
Less than 1,000 square feet |
8,000 to 10,000 kWh |
|
Medium Home |
1,000 to 2,000 square feet |
10,000 to 14,000 kWh |
|
Large Home |
More than 2,000 square feet |
14,000 to 18,000 kWh |
- Number and Efficiency of Home Appliances
The number of appliances and devices you use in your home can significantly impact your electricity usage. The more appliances and devices you have in your home, the more electricity you use.
Additionally, older appliances are often less energy efficient than newer ones, which can lead to increased electricity usage. Upgrading to more energy-efficient appliances can significantly reduce a home's electricity consumption.
- Climate
The climate conditions where a home is located can impact the electricity consumed. Extreme temperatures, whether hot or cold, require more use of the heating or air conditioning system, which increases kilowatt-hour consumption.
Additionally, heating or cooling needs are directly affected by outdoor temperatures, so the quality of a house's insulation and the type of windows it has play a key role in determining the required temperature to maintain. For example, a well-insulated home will retain heat more effectively during colder months, reducing the need for overheating.
- Lifestyle Habits
Lifestyle habits (which often include activities such as cooking, bathing, and entertainment preferences) are also essential factors in electricity consumption. So, consumers can make conscious choices to reduce electricity consumption by developing energy-saving habits and understanding their electricity usage patterns.
What Appliances Use the Most Electricity in The UK?
Understanding the average amount of electricity used by common household appliances is vital to keeping track of your overall electricity consumption at home. Today's living rooms are filled with small electronic devices that people use frequently, such as game consoles, TVs, mobile phones and tablets.
Wet appliances in the bathroom are also energy-intensive, with appliances such as washing machines, showers and tumble dryers typically using around 16% of total energy consumption. Kitchen appliances (including fridges, freezers, hobs, ovens, kettles, microwaves, etc.) account for around 17% of the average household's electricity bill.

Have you ever wondered which common household appliances use the most electricity? Here's an overview of the most common appliances that use the most electricity in UK homes:
Lighting
Typically, traditional light bulbs consume an average of 31kWh per year, while LED lighting consumes 9kWh annually. So, switching to efficient LED bulbs can help reduce electricity consumption.
Electronics
Devices such as computers, TVs, and game consoles account for around 6% of household electricity consumption. Still, their actual usage depends on the device's power rating and how long it is used.
An LCD flat-screen TV is estimated to consume an average of 199kWh annually. However, a 32-inch LED TV consumes an average of 50kWh per year.
Washing and Drying
Washing machines and tumble dryers consume more electricity, but their consumption depends on their efficiency rating and how often they are used. In the UK, a washing machine consumes 166kWh annually, and the average tumble dryer consumes 394kWh annually.
Cookers
Cooking appliances such as hobs, ovens, kettles and microwaves account for around 4% of electricity consumption. For example, an electric stove consumes an average of about 317kWh annually.
Refrigerators and Freezers
Refrigerators and freezers are everyday household items that account for around 13% of electricity consumption when running continuously. A typical combination fridge uses around 427 kWh per year. However, if you have a refrigerator and freezer with an A+ energy efficiency rating, you might need around 200kWh per year.
How to Reduce Your kWh Usage in The UK?
With the rising cost of living and electricity bills, you can look for ways to reduce your electricity consumption. Although many variables are beyond your control, there are still specific ways to reduce electricity consumption. Here are some practical tips to help you reduce your kilowatt-hour consumption:
Reduce Unnecessary Electricity Consumption
Many electronic devices also consume electricity when they are not unplugged, which is called intermittent or vampire power consumption. So always remember to turn off power-hungry devices when not in use, rather than leaving them in standby mode and wasting more electricity.
Thermostat Settings
Lowering your thermostat in the winter and raising it in the summer can significantly reduce kWh usage. For example, lowering your thermostat by one °C can save 10% on your electricity bill.
Energy-efficient Appliances
To limit your electricity usage (reduce your electricity consumption), replace old, inefficient appliances with energy-efficient ones or switch common household appliances to energy-saving mode.
Take Advantage of Nature
Take advantage of natural light and airflow to reduce electricity use. For example, open curtains and blinds during the day to maximise natural light and airflow and decrease the consumption of artificial lighting and air conditioning.
Insulation
Insulating your home to some extent and installing stormproof windows and doors can reduce heat loss and electricity consumption.
Reduce Water Heating
Heating hot water is a vast electricity consumer. The less hot water you use, the less electricity your hot water system will need to heat it. You can also save electricity by using water-saving devices, such as low-flow shower heads, and by fixing leaks promptly.
Washing and drying clothes typically accounts for around 12% of UK household electricity use. Washing clothes at 30 degrees Celsius instead of 40 degrees Celsius can help reduce electricity consumption. Doing one less load of laundry per week can save £5 per year on your electricity bill. Also, air-drying clothes instead of a tumble dryer can significantly reduce electricity consumption.
Solar Energy
The most significant way to reduce kWh consumption is to use solar energy to replace some or all of your primary electricity needs.
Solar energy systems are flexible tools that convert solar energy into electricity, providing an alternative when there is a power outage or when electricity is needed. In addition, the self-sufficient nature of solar energy systems, like Jackery Solar Generator, reduces dependence on traditional electricity supplies to some extent.
Jackery Solar Generators for Saving kWh Usage
There are many ways to save your electricity consumption in your home or during outdoor activities. Besides having energy-saving awareness and habits, it is reasonable to choose a solar generator to charge essential appliances to save electric bills effectively.

Jackery Solar Generators are comprised of SolarSaga Solar Panels for solar energy capture and Explorer Portable Power Stations for energy storage for further utilisation. The generator can power multiple appliances, such as refrigerators, TVs, lights, etc.
Here, we recommend Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus, 1000 Plus, and 500.
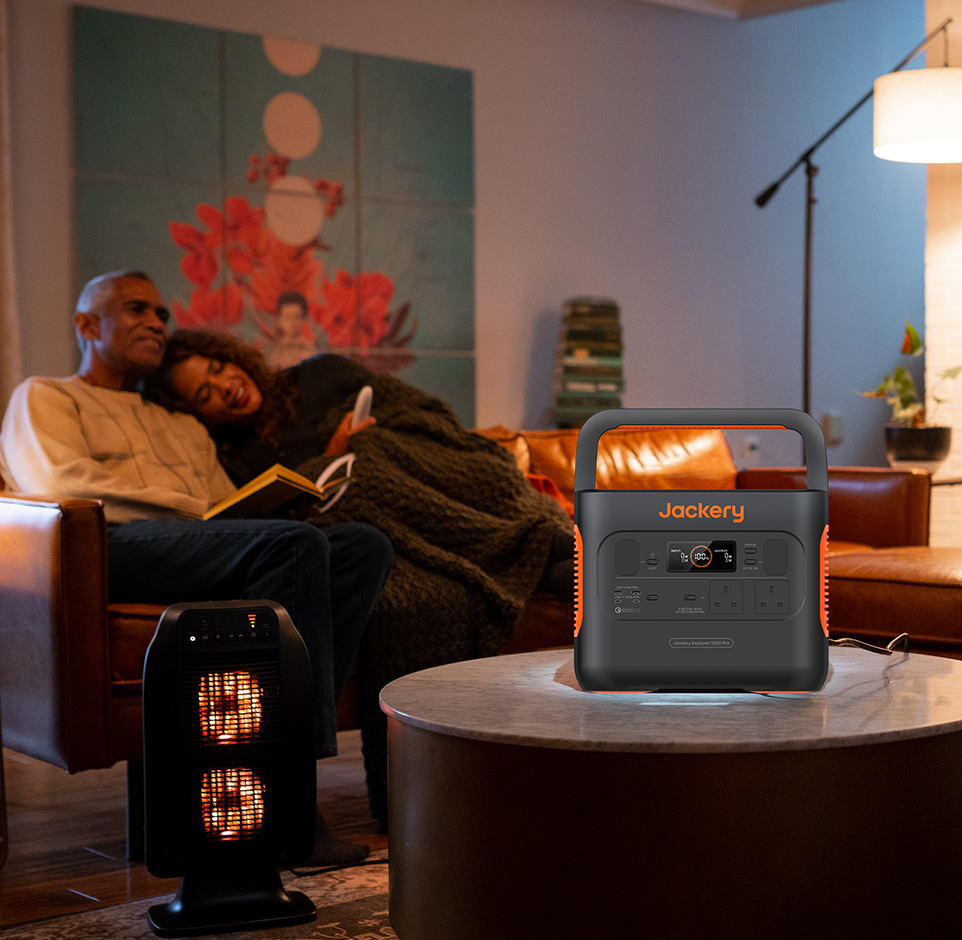
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus
Jackery has introduced the Solar Generator 2000 Plus, a solid portable power solution that delivers outstanding performance. With its impressive capacity and powerful output, this device can support the operation of typical household appliances for weeks, which is best for saving kWh usage in your house.

- Expandable Powerhouse for Your Appliances: The Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus enables the addition of extra battery packs, increasing the capacity from 2 kWhto an impressive 12 kWh, thereby significantly improving the solar charging capabilities. This solar product has a remarkable output of 3000W, providing a 30% higher rated power than other 2 kWh solar products. Almost all necessary household appliances are powered.
- Safe to Use with ChargeShield: ChargeShield is Jackery's advanced fast charge technology, featuring 62protective mechanisms, 12 protective algorithms, and four types of physical safety protection. This technology uses a unique stepped variable-speed charging algorithm to enhance safety and extend battery pack lifespan by 50%.
- Higher Resistance & Reliability: The Explorer 2000 Plus stands out as a groundbreaking add-on battery pack that offers the convenience of recharging through solar panels. This feature increases versatility, boosts charging efficiency, and shortens charging time.
|
*Review from Our User |
|
I have been using Jackery batteries for a long time. I felt great excitement upon the release of the Explorer 2000 Plus. This marks the inaugural release of an expendable battery system by Jackery. The system supports a capacity of up to 12kWh with a 3000W 120V output or 24kWh with a 6000W 240V output - an ideal enhancement for my home backup system. |
Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus
Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus combines SolarSaga 100W solar panels with Explorer 1000 Plus. We will introduce the two components respectively. If Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus is for charging your appliances for a few weeks, this solar generator is for charging for several days.

- Excellent Power Output: The Explorer 1000 Plus power station boasts an excellent 1264Wh long-lasting LiFePO4 battery and a 2000W full-power pure sine wave inverter, supplying almost all required power. Adding up to three additional battery packs will remarkably increase its capacity to 5kWh.
- Expandable Powerhouse: Adding up to three extra battery packs lets Jackery's exclusive technology boost the Explorer 1000 Plus capacity from 26kWh to5kWh. Moreover, it has a maximum output of 2000W, 20% more than usual 1kWh LFP generators.
- Higher Solar Conversion Rate: The Jackery SolarSaga 100W Solar Panel boasts a solar conversion rate of up to 25%; it is optimally designed for outdoor use and unforeseen power interruptions. The solar panel weighs about 8 lbs, is lightweight, foldable, and equipped with a convenient carry handle, enhancing its portability.
|
*Review from Our User |
|
First, this item is robust and space-efficient, fitting seamlessly in my workspace (see pic). When the power goes out, it becomes a real game changer. I can continue my tasks as if everything is normal, which is quite impressive. The most advantageous aspect for me? The USB-C ports. I can connect my Mac directly to it without needing an adapter. Incredibly useful! |
Jackery Solar Generator 500
Jackery Solar Generator 500 is a little smaller than Solar Generator 2000 Plus or 1000 v2, but it is best for charging small devices. It is a combination of Explorer 500 and SolarSaga 100W solar panels. Check below for more features that enable consistent power for some compact electronics or devices at home.

- Portable Power Solution for Electronics: The Jackery Explorer 500 is one of the lightest and most portable rechargeable lithium battery generators available today. It includes a PURE SINE WAVE 500-wattAC outlet that delivers stable power to various AC-dependent devices, such as portable fans, projectors, coolers, and lights.
- Safe & Strong for Multiple Uses: The Explorer 500 features an emissions-free energy source and a dependable battery management system, ensuring its safety for indoor use. Constructed from robust material, the solar system exhibits resistance to high temperatures. The Explorer 500 power station operates within a temperature range of 14-104℉ (-10-40℃), while the SolarSaga 100 functions between 14-149℉ (-10-65℃).
- Versatile Charging Outputs: This versatile portable power station has three USB ports, a 12V car output, and an AC outlet, ensuring reliable power for your appliances. The power station can be charged through three distinct methods: solar panels, a car outlet, and an AC adapter.
|
*Review from Our User |
|
This brand is reliable and transparent about its capabilities, ensuring it doesn't deplete when unused. I purchased it three years ago and have used it for 200 days yearly, primarily for light tasks. It still retains its charge without any noticeable decline, significantly outperforming my phone. |
kWh Usage in The UK FAQs
The following are the frequently asked questions about the kWh usage for a house in the UK:
- Is there any difference between kW and kWh?
The main difference between kW and kWh is what they measure. kW is a unit of power, which can be thought of as the rate at which energy flows at a specific moment. kWh is a unit of energy used over time, which can be considered the cumulative amount of energy used.
- How many kWh does a UK house use per day?
The typical UK household consumes around 7.4 to 9.9 kWh of electricity daily. The daily electricity usage of a UK household can vary based on factors such as household size, appliances, and the time of year.
- Is 40 kWh per day a lot?
Indeed, 40 kWh per day exceeds the typical electricity consumption in the UK. According to Ofgem, the average home in the UK consumes 7.4 kWh of electricity daily. It's standard for 3,000 square feet or larger homes with five or more occupants to consume 40 kWh or more daily.
- Does kWh consumption vary seasonally in the UK?
There is no doubt that kWh consumption varies seasonally in the UK. Factors such as temperature, hours of sunshine and holiday events can cause kWh consumption to fluctuate.
On hot days, many households tend to consume more electricity due to the increased use of air conditioning. In the cold days, electricity consumption is higher in winter due to the need for heating. High-frequency use of furnaces, electric heaters, and other heating equipment during the winter increases kWh usage.
Final Thoughts
The average kWh consumption of a home depends on different factors, from area and family size to living habits. Therefore, adopting energy-efficient appliances, improving home insulation and using renewable energy are effective measures for UK households to reduce their kWh consumption. If you want to know the kWh consumption of an average household and related information, read this article carefully.