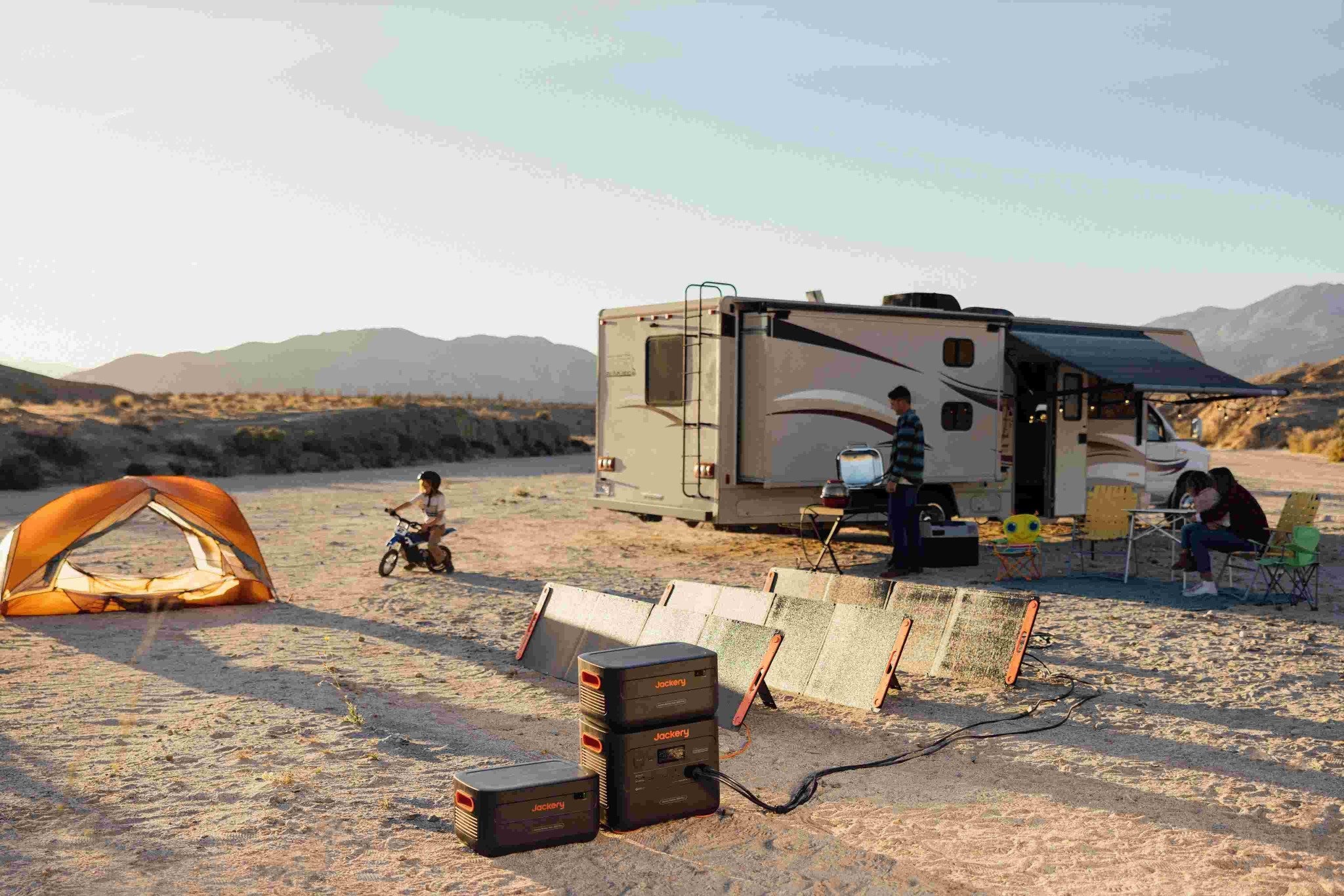
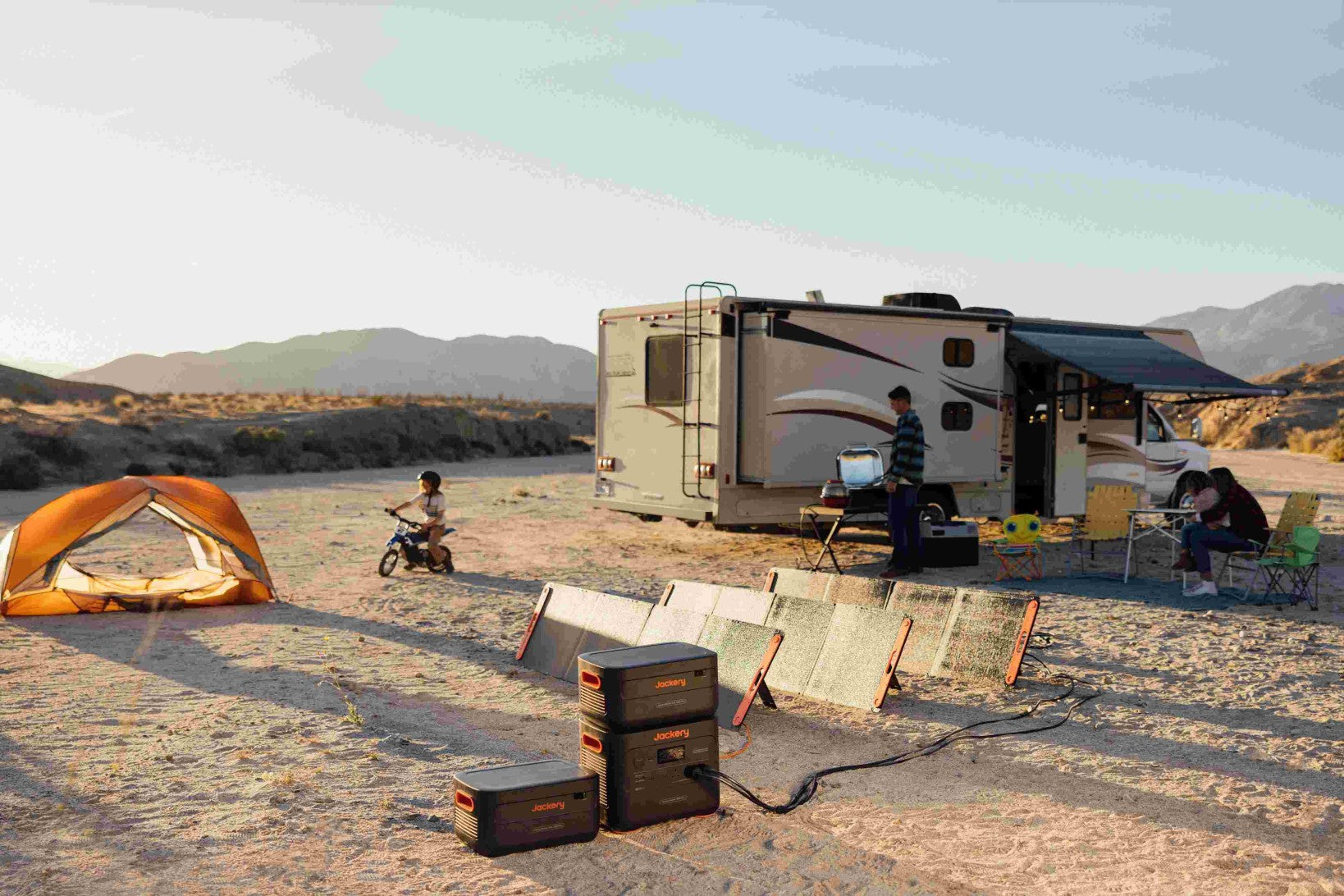
Mini and small fridges offer a convenient way to preserve drinks, cold food, and other items without taking up space or using as much energy as a full-sized fridge. However, you must consider energy consumption when buying a mini fridge. So, how much electricity does a mini and small fridge consume?
In the following article, we will study the power consumption of mini & small fridges and explore the factors that affect power consumption and how to reduce it. We also recommend the Jackery Portable Power Station for powering your refrigerators, whether small or large, at home or outdoors to save electric bills.
|
Key Takeaways: |
|
- A mini and small fridge is a small household or portable refrigerator or a smaller version of a standard refrigerator. - A mini fridge with a power of 50-100 watts consumes about 0.4kWh to 0.8kWh when running for 8 hours a day. - Among common household appliances, the power consumption of a mini fridge is medium to low. - The mini fridge's model and size, the ambient temperature, the number of items stored, and the user's usage habits will affect its power consumption. - Setting the optimal temperature, ensuring a good seal, avoiding heat sources and sunlight, or using solar power can reduce the mini fridge's power consumption. - We recommend the Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus or 2000 v2 portable power station to power your refrigerators or coolers effectively. |
What Is a Mini & Small Fridge?
A mini or small fridge is a small household or portable refrigerator similar to a regular refrigerator or even a smaller version of a standard refrigerator. Its capacity is usually between 10 and 100 litres, which is suitable for storing small amounts of drinks, snacks, cosmetics, medicines, etc.
Generally, mini and small fridges can provide practical solutions for consumers who do not fit or need the space of a traditional refrigerator. For example, they have recently become popular for dormitories or small apartment residents.
Features of Mini & Small Fridge
Here are the main features of mini & small fridge:
Small Size: It takes up little space and can be placed in narrow areas such as desktops, bedsides, offices or dormitories.
Energy Saving and Low Consumption: It has low power consumption and is more energy-saving than traditional refrigerators.
Multiple Functions: Most mini and small fridges only support refrigeration (0℃~10℃), and a few have a freezing function (about -18℃). Some mini and small fridge models can even switch to insulation mode, keeping the temperature between 50℃~65℃, suitable for warm drinks.
Portable Design: Mini fridges usually weigh less than 5kg, and some have handles, making them suitable for camping and travel.
Common Uses of Mini & Small Fridge
The following are common uses of mini & small fridges:
Beverage Refrigeration: Mini & small fridges are often used by people to chill drinks, beer, fruits, etc.
Cosmetic Storage: Some people store facial masks, essences, and other skin care products that need to be stored at low temperatures in mini and small fridges.
Medication Preservation: Insulin, eye drops, and other temperature-sensitive medicines can also be stored in mini and small fridges.
Maternal and Child Use: A mini and small fridge can also store breast milk and baby food.
Outdoor Scene: If you plan to go on a self-driving tour, picnic, or camping, a mini and small fridge can allow you to carry cold drinks or keep food fresh.

Average Power Consumption of Mini & Small Fridge
When evaluating the power usage of a mini and small fridge, you need to consider its power. Power refers to the rate at which the mini and small fridge uses electricity, measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW).
Typically, a mini and small fridge's power is between 50 and 100 watts. Energy consumption refers to the electricity the mini and small fridge consumes over a specific period, measured in watt-hours (Wh) or kilowatt-hours (kWh).
How do you calculate the mini fridge power consumption?
Calculating the power consumption of a mini & small fridge takes just a few simple steps. Here are some simple steps to help you estimate the power consumption of a mini & small fridge:
Step 1: Determine the Power
You can check the instruction manual or the back of your mini & small fridge to find its power.
Step 2: Estimate the Usage Time
Once you have determined the power of your mini and small fridge, choose how many hours it will run each day. Please note that mini and small fridges usually run in cycles rather than continuously, so you must be conservative in estimating their running time.
Step 3: Calculate Power Consumption
Electric power consumption is usually measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), so convert the power of the mini and small fridge (in watts) to kilowatts by dividing it by 1,000. Then, multiply the power of the mini and small fridge by the number of hours it runs per day to find its daily power consumption.
Example: If a 75-watt mini fridge runs for 8 hours per day, how much power does it consume?
Wattage converted to kilowatts: 75 watts/1,000 = 0.075 kilowatts
Daily power consumption of a mini fridge: 0.075 kilowatts*8 hours/day=0.6 kWh/day
Monthly power consumption of a mini fridge: 0.6 kWh/day*30 days/month=18 kWh/month
Annual power consumption of a mini fridge: 0.6 kWh/day*365 days/year=219 kWh/year
Therefore, this mini fridge consumes about 0.6 kWh per day, about 18 kWh per month, and about 219 kWh per year. The power consumption of this 75-watt mini fridge is not significant.
The following are the power consumption of mini fridges of different powers for your reference:
|
|
Estimated kWh Used per Day |
Estimated kWh Used per Month |
Estimated kWh Used per Year |
|
50W Mini Fridge |
0.4 kWh/Day |
12 kWh/Month |
146 kWh/Year |
|
60W Mini Fridge |
0.48 kWh/Day |
14.4 kWh/Month |
175.2 kWh/Year |
|
70W Mini Fridge |
0.56 kWh/Day |
16.8 kWh/Month |
204.4 kWh/Year |
|
80W Mini Fridge |
0.64 kWh/Day |
19.2 kWh/Month |
233.6 kWh/Year |
|
90W Mini Fridge |
0.72 kWh/Day |
21.6 kWh/Month |
262.8 kWh/Year |
|
100W Mini Fridge |
0.8 kWh/Day |
24 kWh/Month |
292 kWh/Year |
(Data Source: Bougerv)
Please note that the above data are estimates and are for reference only. The power consumption of a mini & small fridge is affected by many factors, including model, size, age, energy efficiency, and ambient temperature.
For example, a mini fridge will run longer in the summer than in the winter because it has to contend with a naturally warmer outside environment.
Does Mini & Small Fridge Use a Lot of Electricity?
Mini fridges are a common choice for singles, student dormitories and offices due to their compactness and portability. However, considering the rising electricity bills in recent years, you may wonder if a small fridge consumes a lot of yearly electricity. The following is a comparative analysis of the power consumption of mini fridges and other common household appliances:

Mini Fridge vs. Regular Fridge
The power of a regular fridge is about 120-200 watts, and it runs 24 hours a day without interruption. Without considering factors such as volume, energy efficiency rating and frequency of use, its average daily power consumption is about 2.88-4.8kWh. Mini fridges are usually smaller and lower in power (about 50-100 watts), with an average daily power consumption of about 0.4kWh to 0.8kWh (calculated based on 8 hours of operation).
Therefore, mini fridges consume significantly less power than regular fridges and are suitable for the energy-saving needs of singles or small families.
Mini Fridge vs. Lamps
The power of LED lamps in homes is about 5-20W, while traditional bulbs are about 40-100W. Assuming an LED bulb is used 5 hours daily, its daily power consumption is about 0.025-0.1 kWh. If a conventional bulb is used 5 hours a day, the power consumption is about 0.2-0.5kWh.
Therefore, the power consumption of a mini fridge is much higher than that of an LED lamp but similar to that of a traditional incandescent lamp. If the lamp is used frequently for a short period, the power consumption may be identical to that of a mini fridge.
Mini Fridge vs. TV
Modern LCD TVs have a power of about 50-200W. Assuming they are watched for 4 hours daily, their power consumption is about 0.2-0.8 kWh/day. For example, a 32-inch LCD TV has a power of about 50W, and the average daily power consumption (based on 4 hours of use) is about 0.2kWh. A 55-inch TV has a power of up to 200 watts, and the average daily power consumption is about 0.8kWh.
Therefore, although the power consumption of a mini fridge is similar to that of a TV, it is higher than that of a TV used for a short period.
Mini Fridge vs. Microwave Oven
Compared with small household appliances, microwave ovens have a higher power, usually 800~1200W. If an 800-1200W microwave oven runs for one hour, its power consumption is 0.8kWh to 1.2kWh. However, the single-use time of a microwave oven is short, usually 1-5 minutes. Most people use the microwave oven for about 20 minutes daily, so the power consumption is 0.26-0.4kWh/day.
Therefore, microwave ovens are short-term high-power devices, and their short-term high-frequency power consumption is lower than mini fridges.
Mini Fridge vs. Washing Machine
Today's energy-saving washing machines (such as a 6kg capacity washing machine with a 1-hour washing program) have a single power consumption of about 0.3-0.5 kWh. Assuming it is used 3 times a week, the average daily power consumption of the washing machine is about 0.13-0.21 kWh.
Therefore, the average daily power consumption of a mini fridge in intermittent use is significantly higher than that of a washing machine but lower than that of frequent washing.
|
Electrical Appliances |
Average Daily Power Consumption (kWh) |
Operation Characteristics |
|
Mini Fridge |
0.4-0.8 kWh |
All-day intermittent operation (8 hours/day) |
|
LED Lights |
0.025-0.1 kWh |
Short-term use (5 hours/day) |
|
Washing Machine |
0.13-0.21 kWh |
Intermittent use (3 times a week) |
|
LCD TV |
0.2-0.8 kWh |
Intermittent use (4 hours/day) |
|
Microwave Oven |
0.26-0.4 kWh |
Short-term high power (20 minutes/day) |
|
Regular Refrigerator |
2.88-4.8 kWh |
24-hour continuous operation |
The data in this table are all estimated values for reference only.
Mini fridges are commonly used household appliances. Their power consumption is medium to low, similar to that of a TV or microwave oven, but much lower than that of a regular fridge.
If used for a long time, a mini fridge's total power consumption may be higher than that of a short-term high-power appliance (such as a microwave oven) but much lower than that of a large appliance such as an air conditioner or electric water heater.
Factors that Affect the Power Consumption of Mini & Small Fridge
Although mini & small fridges use less power than full-size fridges, they can sometimes significantly increase your electricity bill. Here is an analysis of the main factors that affect mini fridge power consumption, combined with energy efficiency, usage habits and environmental factors:

Mini Fridge Model and Size
The model and configuration of a mini fridge will affect its cooling effect and power consumption. Generally, mini fridges with higher energy efficiency ratings have higher cooling efficiency and use less power for the same cooling effect.
In addition, the size of a mini fridge is the most critical factor affecting its power consumption. Generally, larger mini fridges use more energy than smaller mini fridges to cool their larger internal space.
Temperature Setting
Some mini fridges have temperature adjustment functions, and low-temperature settings (such as freezer mode) use more power than medium-temperature settings. For example, for every 1°C lower in a mini fridge's set temperature, power consumption increases by about 5%. In addition, some mini fridges require heaters to prevent condensation in low-temperature environments in winter, which may slightly increase power consumption.
Ambient Temperature
Ambient temperature directly affects a mini fridge's energy consumption. The mini fridge must maintain a low internal temperature for longer when the ambient temperature rises, increasing the compressor operation frequency. For example, for every 5°C increase in room temperature, a mini fridge's power consumption may increase by 10% to 20%. Summer or hot environments (such as kitchens) will cause mini fridges to be more loaded.
Cooling Space
Mini fridges usually dissipate heat through the sides or back. If they are close to the wall or cluttered, they will hinder the mini fridge's heat dissipation and cause the compressor to overload. Placing mini fridges in a cool place can improve efficiency and reduce power consumption.
Frequency of Use
The number of times you open and close the mini fridge door may affect the fridge's power consumption. Frequent opening and closing will cause about 30% of the cold air to be lost, forcing the compressor to start frequently to replenish the chilly air, increasing energy use. If the mini fridge door is opened and closed more than 20 times daily, it may increase power consumption by 15% to 30%.
Items Storage
Too many items in the refrigerator will increase the cooling load, while too few items may cause temperature fluctuations. Generally, excessive stacking hinders the circulation of cold air in the mini fridge and increases energy consumption. For example, a 50L mini fridge consumes about 0.3-0.5kWh/day when unloaded and may double when fully loaded.
Usage Habits
A thick layer of frost (more than 5mm) inside a mini fridge usually hinders the evaporator's heat exchange and increases power consumption. The ageing of the door seal will also cause air leakage and increase energy consumption. In addition, the compressor efficiency of a mini fridge that has been used for more than 5 years may decrease by 20%, and power consumption will increase significantly.
How to Reduce the Power Consumption of Mini & Small Fridge?
Reducing your mini fridge's energy consumption can save money and help the environment. Here are some tips to help you save energy and money while keeping your mini fridge running smoothly.

Tip 1: Set the Best Temperature
Ensure your mini fridge is set to the best temperature to keep food fresh. For example, it is recommended to set the refrigerator to 4-5°C and the freezer to -18°C—the power consumption increases by about 5% for every degree the temperature drops. If the ambient temperature is low (such as in winter), you can adjust the setting to a higher level to avoid overrunning the compressor.
Tip 2: Ensure a Good Seal
Ageing or deformation of the mini fridge door seal can cause cold air to leak out and increase power consumption. You can test the seal with a piece of paper every month. The seal must be replaced or cleaned if the paper can be easily pulled out or slipped off. In addition, wipe the door frame regularly with warm water and soap to prevent dust from affecting the seal.
Tip 3: Keep Away from Heat and Sunlight
Avoid placing it in direct sunlight or near heat sources such as ovens, stoves, and heaters. In addition, leave at least 5 cm of space at the back, top, and sides of the fridge to ensure good air circulation. Place a mini fridge in a well-ventilated area without direct sunlight.
Tip 4: Reduce Door Openings
Avoid opening the mini fridge door too often and only open it when necessary. In addition, limiting the time the mini fridge door is open can prevent cold air loss and reduce the compressor's workload, thereby saving energy. For example, each time you open the mini fridge door, control the time to less than 15 seconds and avoid leaving it open for long periods. Plan before taking out items, and take out the items you need at once to reduce the loss of cold air.
Tip 5: Arrange Items Properly
Although putting more things in the mini fridge can help it retain more cold air, overstuffing it will prevent air from flowing freely, causing the refrigerator to consume too much energy.
In addition, hot food needs to be cooled before adding it to avoid increasing the internal temperature. Freezer food can also be packaged in small plastic bags to speed up freezing and prevent frost.
Tip 6: Clean Regularly
A clean mini fridge ventilates more smoothly and uses less energy, so please clean it regularly to improve its operating efficiency. For example, use a soft-bristle brush to clean the dust from the condenser on the back or bottom every six months and regularly clean the frost layer on the mini fridge. After defrosting, wipe the interior with a soft cloth to keep the evaporator clean. In addition, you need to clean expired or spoiled items in the mini fridge regularly.
Tip 7: Using Solar Energy
Solar energy is a more environmentally friendly and economical way to power your mini fridge. You don't have to pay for the electricity to run the refrigerator because the sun can power it for free. For example, you can use the Jackery Explorer 2000 v2 Portable Power Station with a solar panel to power your mini fridge for free.

Jackery Portable Power Stations for Mini & Small Fridges
Unlike gasoline generators, the Jackery Portable Power Station operates silently and produces no exhaust fumes, making it safe for indoor use and more pleasant for outdoor environments. Jackery offers a clean energy solution, creating no noise or fumes. This is a significant advantage over gasoline generators, especially for indoor use or in quiet outdoor settings.
A Jackery Portable Power Station can serve as a reliable backup power source for small fridges during short to medium-length power outages, helping to prevent food spoilage. The runtime will depend on the power station's capacity and the fridge's energy consumption.
For situations where you don't have access to traditional electricity, such as camping or working remotely outdoors, a Jackery Portable Power Station paired with Jackery Solar Panels (sold separately) can provide a sustainable way to power a small fridge.
Jackery Explorer 2000 v2
The Jackery Explorer 2000 v2 is a powerful portable power station with a substantial 2042Wh capacity and a 2200W continuous output (4400W peak). This robust capability makes it a viable option for powering refrigerators of various sizes.

Extended Runtime: Mini and small fridges typically have lower power consumption (e.g., 50-150W running wattage). The Explorer 2000 v2 can power these for significantly longer durations than smaller power stations, making it ideal for extended camping trips, RV use, or a reliable backup during more extended power outages. Depending on its specific power draw and duty cycle, you could run a small, efficient fridge for over 10 hours, if not a whole day.
Substantial Backup Power: Medium-sized refrigerators (e.g., 150-400W running wattage) can also be powered by the Explorer 2000 v2 for valuable time during power outages. While the runtime will be shorter than smaller fridges, it can still help preserve your food for several hours, potentially overnight or longer, depending on the fridge's efficiency and how often the compressor runs.
Off-Grid Capabilities: For RVs or off-grid setups with medium-sized fridges, the Explorer 2000 v2 can offer a more sustainable power solution, especially when paired with solar panels for recharging. The high peak output is crucial for the initial power draw when the fridge compressor starts.
Emergency Backup (Limited Runtime): While large, full-sized refrigerators (e.g., 400-800W running wattage or higher) have significant power demands, the Explorer 2000 v2 can still provide valuable emergency backup power for a few hours. This can be critical to prevent food spoilage during short to medium-length outages.
|
Jackery Explorer 2000 v2 Running Time (2042Wh) |
|
|
Mini & Small Fridge (50-150W) |
10-24.6H |
|
Medium Fridge (150-400W) |
4-10H |
|
Large Fridge (400-800W) |
2-4H |
|
Portable Cooler (60W) |
21.5H |
(*The working hours are only for reference; the actual working hours depend on your usage.)
Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus
With its high continuous output of 3000W and peak of 6000W, the Explorer 2000 Plus can easily handle the running and starting wattage of mini, small, medium, and even most large refrigerators. Moreover, the expandable capacity from 2 to 12 kWh makes the 2000 Plus more suitable for home backup, off-grid living, or emergency use.

Portable Powerhouse: The substantial 2042.8 Wh capacity provides significant runtime for refrigerators, especially smaller and more energy-efficient models. For example, it can power a small car fridge for over 20 hours. Even larger fridges offer hours of crucial backup during power outages.
Expandable Capacity for Longer Needs: A standout feature is its expandability. You can add up to five additional Jackery Battery Pack 2000 Plus units, increasing the total capacity to a massive 12 kWh, providing days of power for even larger refrigerators and other household appliances.
Seamless Power with UPS: The built-in UPS function ensures that your refrigerator continues running without interruption during a power outage, preventing food spoilage. With the proper setup, it can be quickly recharged via AC power or, for a sustainable solution, through solar panels in as little as 2 hours.
|
Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus Running Time (2-12 kWh) |
|
|
Mini & Small Fridge (50-150W) |
10-192H |
|
Medium Fridge (150-400W) |
4-64H |
|
Large Fridge (400-800W) |
2-24H |
|
Portable Cooler (60W) |
21.5-160H |
(*The working hours are only for reference; the actual working hours depend on your usage.)
FAQs about Mini & Small Fridges
The following are the frequently asked questions about the mini & small fridges.
1. How much power does a mini & small fridge consume?
Most mini fridges run at around 50-100 watts, so the power consumption for one hour is around 0.05-0.1 kWh. Since mini fridges run intermittently throughout the day, it is not possible to calculate based on a 24-hour running time.
Assuming a mini and small fridge with a running power of around 50-100 watts runs for 8 hours a day, the power consumption is around 0.4-0.8 kWh. However, this is only an estimate, and the specific power consumption depends on factors such as the size of the fridge, usage level, age, and energy efficiency.
2. What is the typical lifespan of a mini & small fridge?
In theory, the typical lifespan of a mini & small fridge is around 5 to 10 years. However, its durability is affected by many factors. For example, frequent switching on and off in a hot and humid environment will accelerate its wear and shorten its lifespan. Regular cleaning and ensuring good ventilation can extend its lifespan.
3. Is it safe to place a mini & small fridge in a bedroom?
Generally, placing a mini and small fridge in a bedroom does not pose a significant safety risk. However, putting them in the sleeping space will mainly affect sleep because they may make noise.
4. What alternatives can I use instead of a mini & small fridge?
If you are planning a short trip or a picnic or have a temporary refrigeration need, you can choose an incubator or ice bucket instead of a mini and small fridge. They do not require power, are highly portable, and only rely on ice packs or ice cubes to keep warm. However, the insulation time of incubators and ice buckets is limited, and they are only suitable for short-term use.
Final Thoughts
Unlike traditional refrigerators, mini and small fridges are smaller, more space-saving, and portable, making them ideal alternatives. Therefore, whether in dormitories, garages, or off-grid locations, people are willing to use a mini and small fridge to keep food and drinks fresh.
Please note that high ambient temperature, too many items stored, and frequent use will affect the power consumption of mini fridges. Setting the optimal temperature, ensuring good sealing, keeping away from heat sources and sunlight, and using solar power can effectively reduce the power consumption of mini fridges.