From running appliances to providing heat and light for people to powering the appliances themselves, electricity consumption is an integral part of everyday life. As a highly industrialised and urbanised country, the UK's electricity consumption has always been a focus of attention.
Have you ever wondered what the average UK household uses? Is using 20 kWh of electricity a day too much in the UK? Or have you ever thought about which appliances might be the ones consuming the most electricity in your home? Understanding your home's electricity consumption will help control costs and make your home more energy-efficient.
|
Key Takeaways: |
|
- Economic, technological and policy factors influence electricity consumption in the UK. - The 20 kWh of daily electricity consumption is relatively high. - The UK's overall electricity demand has gradually declined since its peak in 2005, from 406 terawatt hours (TWh) 2005 to 330 TWh in 2020. - The average UK 1 household uses around 2,900 kWh of electricity per year, and the average UK 2 household uses around 4,200 kWh of electricity per year. - We recommend the Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus or 2000 Plus to charge your appliances with solar energy and save on electric bills. - High electricity users usually consume a lot of electricity during specific periods. |
Electricity Consumption in the UK
In recent years, the UK has made some progress in reducing electricity consumption, improving energy efficiency and promoting renewable energy.
The UK's electricity demand has gradually declined since its peak in 2005, from 406 terawatt hours (TWh) in 2005 to 330 TWh in 2020. Since 2010, industrial and household electricity consumption has fallen by more than 12%.
With the popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) in recent years, electricity consumption in the transportation industry increased by nearly 10% between 2018 and 2019. In addition, the business and service industries are important areas of electricity consumption.
Sources of Electricity in the UK
The UK's electricity sources include natural gas, nuclear, and renewable energy. However, in recent years, renewable energy development has been strong, and the installed capacity of wind and solar power has continued to increase.
To achieve this goal, the UK is building large-scale wind and solar power generation facilities and upgrading existing hydropower and geothermal facilities. In addition, the UK plans to phase out all remaining coal-fired power stations by 2025.
Future Development of UK Electricity Consumption
The trend of electricity consumption in the UK will continue to be influenced by economic, technological and policy factors. Therefore, the UK is expected to increase the proportion of renewable energy further and reduce electricity consumption and carbon emissions. In addition, the UK also needs to strengthen grid construction and intelligent management to ensure the stability and reliability of power supply.
Average Electricity Consumption in a UK Household
In recent years, with the fluctuation of energy prices and the implementation of low-carbon policies, the average electricity consumption of British households has received widespread attention. Although electricity consumption may vary due to household size and lifestyle factors, people usually use average electricity consumption to measure whether electricity consumption is too high.
There are nine electricity consumption profiles in the UK, but only two (Profile 1 and 2) are related to household use. However, the average electricity consumption under different profiles is also different.
Profile 1 (Electricity Profile Class 1)
Profile 1 is unlimited household electricity use; most households belong to this category. In addition, households in the Profile 1 category usually have lower electricity consumption.
Profile 2 (Electricity Profile Class 2)
Profile 2 covers household economy 7. These households have installed economy 7 meters ("time of use"), and they have lower electricity bills during off-peak hours at night.
|
|
Profile 1 Usage (in kWh) |
Profile 2 Usage (in kWh) |
|
Low Consumption Rate |
1,800 kWh |
2,400 kWh |
|
Medium Consumption Rate |
2,900 kWh |
4,200 kWh |
|
High Consumption Rate |
4,300 kWh |
7,100 kWh |
According to Ofgem, the average UK Profile 1 household uses around 2,900 kWh of electricity per year, and the average UK Profile 2 household uses around 4,200 kWh of electricity annually.
Is 20 kWh of Electricity a Lot Per Day in the UK?
Due to soaring energy prices and the tight power supply, the issue of electricity consumption in the UK has become a hot topic.
In the UK, household electricity consumption mainly includes the following aspects: Heating and hot water account for about 40% to 50% of the total electricity consumption. The high electricity consumption for heating and hot water is because the UK has long winters with low temperatures, and households need a lot of energy to keep homes warm and supply hot water. Lighting and household appliances each account for 20% to 25% of the total electricity consumption; the rest is used for cooking and other purposes.
Is 20 kWh of Electricity a Lot Per Day in the UK?
So, for an average household or business, what is the level of electricity consumption of 20 kWh per day in the UK? Is this a lot of electricity?
A rough average can be calculated based on the average electricity consumption data of Profiles 1 and 2. In short, the average electricity consumption of an average British household is 10kWh per day (estimated). It includes lighting, heating, cooling, cooking, and various household appliances.
Therefore, in the UK, 20 kWh of electricity per day is a relatively high value for an average household. For most UK households, 20 kWh of electricity consumption is almost 100% above the average.
Why Is 20 kWh of Electricity Consumed a Lot in the UK?
Based on the above, if a UK household uses 20 kWh of electricity daily, they may use 8 to 10 kWh for heating and hot water and 4 to 5 kWh for lighting and household appliances. Such electricity consumption levels may indicate that the family has a larger living space that requires more energy to heat and keep comfortable or that they have more high-energy appliances, such as large TVs, multiple computers, game consoles, and other high-powered devices.
From an environmental and energy-saving perspective, 20 kWh of daily electricity consumption also means higher carbon emissions. The UK National Grid states that each kWh of electricity consumption produces approximately 0.4 kg of carbon dioxide emissions. It puts more significant pressure on the environment and means the household's electricity bill will be relatively high.
In summary, 20 kWh of electricity consumption per day is relatively high in the UK. However, this figure can be judged as something other than more or less and needs to be analysed based on specific circumstances. In addition, with the current high energy prices and tight electricity supply, reducing electricity consumption and improving energy efficiency have become a general trend in British society.
How To Determine Whether You Are a High-Energy User?
Many people in the UK wonder if they are high-energy users. In the UK, a high electricity user generally uses a lot of electricity over time. It can include large commercial establishments, industrial businesses, and specific residential users.
Based on Ofgem's common energy user groups, you can assess whether you are a high, medium, or low-energy user. Here is a brief description of the different energy user levels in the UK from Ofgem:

Low Energy Users
Low-energy users use the least energy on average because they only use the heating occasionally and do not use a dishwasher or tumble dryer. In addition, low-energy users are usually one or two people living in a one—or two-bedroom apartment who are home at night and on weekends and do laundry once a week.
Medium Energy Users
Medium-energy households usually consist of three to four people living in a three-bedroom house. They use electrical appliances frequently, such as washing clothes three times a week on average.
High Energy Users
On average, the households that use the most energy tend to be large families with five or more people living in a four-bedroom or larger house. High-energy users have someone always home during the day and someone always home at night and on weekends. They may use several appliances simultaneously and frequently use tumble dryers and dishwashers.
Factors Affecting Electricity Consumption in the UK
In the UK, household electricity consumption has always been affected by several factors. These factors include weather, seasonal changes, and economic, technological, and social behaviour.
Understanding these factors can help formulate more effective energy policies and promote sustainable energy development while also assisting households in better managing electricity consumption and reducing living costs. Here are some of the main factors affecting household electricity consumption in the UK:

House Size
It is known that the size of a house significantly affects electricity consumption. Due to their various sizes, each home has different heating and lighting requirements. The bigger the house, the more electricity you need to meet your needs. Typically, a spacious mansion will naturally consume more electricity than a compact city apartment.
|
Type of Home |
Size of Home |
Average Annual Electricity Usage |
|
Small home or apartment |
Apartment or 1 bedroom home |
1,800 to 2,400 kWh |
|
Medium home |
2-3 bedroom home |
2,900 to 4,200 kWh |
|
Large home |
4+ bedroom home |
4,300 to 7,100 kWh |
Family Size
Household size (the number of people living in a home) can significantly affect a home's electricity usage. More people living in a home typically means more appliances are used, more lights are turned on, more hot water is needed, and more heating or cooling is required. For example, a family of five typically consumes more electricity than three living in a similarly sized house.
Efficiency of Household Appliances
The types of appliances you use in your home, and their efficiency significantly impact your electricity consumption. With the development of science and technology, more and more high-efficiency and energy-saving appliances have entered the market, which can consume less electricity while providing the same service.
For example, LED lighting saves about 80% more energy than traditional incandescent bulbs. In addition, the development of smart home systems has also enabled households to manage electricity consumption more effectively and reduce waste through remote control and automation systems.
The table below shows the appliances commonly used in UK households that consume the most electricity:
|
Common Household Appliances |
Monthly Electricity Consumption |
|
Tumble dryer |
52.25 kWh |
|
Dishwasher |
40 kWh |
|
Refrigerator |
35.42 kWh |
|
Washing machine |
35 kWh |
|
Oven |
24.16 kWh |
|
Computer |
14.16 kWh |
|
Electric kettle |
13.75 kWh |
Living Habits
British lifestyle habits, which often include cooking, bathing, and entertainment preferences, are also essential factors that affect household electricity consumption. In other words, how you use appliances and when they are most active can significantly affect electricity usage. For example, Britons like to watch TV and use the Internet in the evenings and weekends, which causes a significant increase in electricity consumption during these times.
Seasonal Changes
Heating and cooling equipment has become critical to British household electricity consumption. For example, in winter, most British households use electric heaters, water heaters and lighting equipment to keep warm, which directly leads to increased electricity consumption. According to data from National Grid, average household electricity consumption in winter is about 20% higher than in summer.
Government Policies and Regulations
The British government has launched a series of energy-saving policies and regulations (such as carbon emission reduction targets and subsidies) to encourage households to use energy-saving appliances to reduce electricity consumption. In addition, the government regulates household electricity consumption through tax and electricity price policies.
How To Reduce Home Electricity Usage in the UK?
As household appliances become more popular and common, household electricity consumption continues to increase, increasing electricity bills and putting greater pressure on the environment. Although many variables are beyond your control, there are still specific ways to reduce electricity consumption. Here are some practical ways to help you reduce electricity consumption:

Tip 1: Use Energy-saving Appliances
To limit electricity consumption, replace old, inefficient appliances with energy-saving appliances or switch ordinary household appliances to energy-saving mode. In addition, buying and using energy-saving appliances is an effective way to reduce household electricity consumption.
For example, energy-saving lighting usually means replacing traditional light bulbs with modern LED lighting, which consumes less electricity. LED bulbs can help you save a lot of electricity. You can also choose an intelligent lighting control system to light up at specific times.
Tip 2: Reduce the Standby Time of Appliances
Many appliances also consume electricity when they are in standby mode. Although the power consumption of a single appliance is not large, it is also a considerable number when accumulated.
Therefore, please turn off the power of appliances when not in use, especially entertainment equipment such as TVs, computers, and stereos. Items such as smart plugs or standby savers are convenient for cutting off the power of multiple appliances at once to avoid standby power consumption.
Tip 3: Use Air Conditioning and Heating Properly
Air conditioning and heating are significant electricity users in British households, so using them properly can effectively reduce electricity consumption. For example, in the British summer, it is recommended to set the air conditioning temperature at around 26℃. Every 1 degree Celsius increase can reduce the electricity load by about 8%.
In addition, you can install high-quality insulation materials and double-glazed windows for your home, which will help reduce cooling and heating costs.
Tip 4: Check Electrical Equipment Regularly
Electrical equipment may have problems after long-term use, such as ageing and damage, resulting in power waste. Check the working status of electrical equipment regularly to ensure its regular operation.
Replace severely aged equipment in time and clean electrical equipment regularly to improve its working efficiency and reduce electricity consumption. For example, periodically cleaning the air conditioning filter to keep it in good working condition can save electricity.
Tip 5: Use Smart Meters
Installing smart meters can help British households monitor their electricity consumption, identify high-power consumption periods and equipment through data analysis, and make targeted adjustments. Smart meters can also advise electricity usage, helping more UK households optimise their electricity habits and reduce waste.
Tip 6: Use Clean Energy
The most important way to reduce electricity consumption is to use renewable energy to replace some or all of your primary electricity needs. Today, many people use solar systems to save energy because solar power is economical and environmentally friendly.
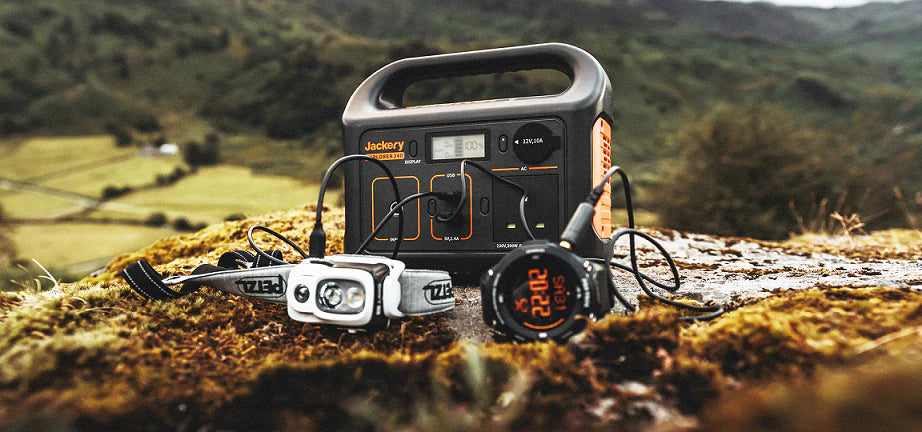
Solar generators provide a renewable way for your home to reduce its reliance on the grid. Investing in a good solar generator, like Jackery Solar Generator, ensures that you can collect and store enough solar energy to reduce your electricity consumption significantly.
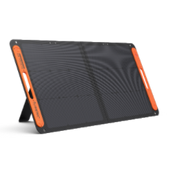
Jackery Solar Generators for Lowering Electric Bills
Solar generators can reduce electric bills by generating electricity that satisfies a household's energy requirements, decreasing electricity expenses. Solar systems generate energy at the point of consumption, thereby circumventing expensive transmission infrastructure. Portable solar generators offer a reliable power supply during power outages or emergencies.

Jackery is a manufacturer of solar products. It has solar panels, solar generators, and portable power stations. A Jackery Solar Generator combines Jackery Solar Panels with a Portable Power Station to turn sunlight into electricity. If you worry about bad weather, wall outlets or carports can refuel the portable power station.
|
|
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus |
Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus |
|
Capacity |
2042.8Wh (expandable to 12 kWh) |
1264Wh (expandable to 5 kWh) |
|
Cell Chemistry |
LFP (LiFePO4 battery) |
LFP (LiFePO4 battery) |
|
Cycle Life |
4000 cycles to 70%+ capacity |
4000 cycles to 70%+ capacity |
|
Dimension |
14.7x14.1x18.6 in |
11.14x10.24x14 in |
|
Recharging Methods |
Explorer 2000 Plus + 6*SolarSaga 200W: 2H; Wall charging: 1.7H; Car charging: 25H |
Explorer 1000 Plus + 4*SolarSaga 200W: 2H; Ultra-fast wall charging: 100 min; Car charging: 14.5H |
|
Output Ports |
3*AC Output: 230V~ 50Hz, 3000W Max, 6000W surge peak; 2*USB-A: Quick Charge 3.0, 18W Max; 2*USB-C: 100W Max, (5V, 9V, 12V, 15V, 20V up to 5A); 1*Carport: 12V⎓10A |
2*AC Output: 230V~ 50Hz, 8.7A, 2000W Rated, 4000W Surge peak; 2*USB-A: 18W Max, 5-6V⎓3A, 6-9V⎓2A, 9-12V⎓1.5A; 2*USB-C: 100W Max, 5V⎓3A, 9V⎓3A, 12V⎓3A, 15V⎓3A, 20V⎓5A; 1*Carport: 12V⎓10A |
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus is the ideal generator for home use, a solid portable power solution that delivers outstanding performance. With its impressive capacity and powerful output, this device can support the operation of essential appliances for weeks, even certain large appliances, such as your refrigerator, computer, AC, etc.
The Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus enables the addition of extra battery packs, increasing the capacity from 2 kWh to an impressive 12 kWh, thereby significantly satisfying your power needs. This solar product has a remarkable output of 3000W, providing a 30% higher rated power than other 2 kWh solar products.
ChargeShield is Jackery's advanced fast charge technology, featuring 62 protective mechanisms, 12 protective algorithms, and four types of physical safety protection. This technology uses a unique stepped variable-speed charging algorithm to enhance safety and extend battery pack lifespan by 50%.
The Explorer 2000 Plus stands out as a groundbreaking add-on battery pack that offers the convenience of recharging through solar panels. This feature increases versatility, boosts charging efficiency, and shortens charging time.
The following image shows the working hours of using Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus to charge essential household appliances:

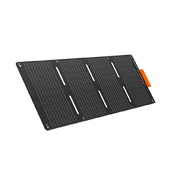
Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus
Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus combines SolarSaga 100W solar panels with Explorer 1000 Plus. The Explorer 1000 Plus is the same as the Explorer 2000 Plus, which is the expandable LiFePO4 battery to be added to a 5 kWh capacity. If Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus is for charging your appliances for a few weeks, this solar generator is for charging for several days.
The Explorer 1000 Plus power station boasts an excellent 1264Wh long-lasting LiFePO4 battery and a 2000W full-power pure sine wave inverter, supplying almost all required power. Adding up to three additional battery packs will remarkably increase its capacity to 5kWh.
Adding up to three extra battery packs lets Jackery's exclusive technology boost the Explorer 1000 Plus capacity from 1.26kWh to 5kWh. Moreover, it has a maximum output of 2000W, 20% more than usual 1kWh LFP generators.
The Jackery SolarSaga 100W Solar Panel boasts a solar conversion rate of up to 25%; it is optimally designed for outdoor use and unforeseen power interruptions. The solar panel weighs about 8 lbs, is lightweight, foldable, and equipped with a convenient carry handle, enhancing its portability.
The following image shows the working hours of using Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus to charge essential household appliances:

FAQs
The following are the frequently asked questions about electricity consumption in the UK:
- What is 20 kWh usage?
Kilowatt-hour is a unit of electrical energy, with the symbol kWh or kW·h. Consuming 20 kWh of electricity means using 20 kilowatts in one hour. For example, if a device with a power of 20 kilowatts runs for one hour, it consumes 20 kWh of electrical energy.
- What is a good kWh rate in the UK?
A relatively reasonable electricity price should cover the cost of electricity production while considering residents' affordability. On this basis, the government can stabilise electricity prices through policy tools such as subsidies and price caps to ensure the regular electricity demand of residents and businesses.
The table below shows unit prices in different regions of the UK, including electricity price data from recent years.

- How many kWh a day is normal?
In the UK, an average household uses around 10kWh of electricity daily. But this is just a rough average, and electricity usage will differ depending on household size, lifestyle, housing type, and season.
For example, a smaller household might use 10 to 15 kWh a day, while a larger household with special electricity needs (such as an electric heater or swimming pool) might use 15 to 20 kWh or more.
Final Thoughts
In recent years, as energy prices have risen, more and more UK residents have taken measures to reduce their electricity usage. Understanding how much electricity UK households consume daily is key to managing home energy consumption and spending costs. In short, in this era of uncertainty in electricity supply, a backup power supply, like Jackery Solar Generator, is an excellent strategy instead of always relying on the grid.