Harnessing solar power often seems complicated, filled with anxieties about inverter reliability, confusing compatibility issues with solar panels, and the hidden costs of traditional, professionally installed systems.
This guide demystifies the world of the solar inverter. It will walk you through everything from traditional grid-tied systems to modern, all-in-one solar generators.
What is a Solar Inverter and Why is it Essential?
A solar inverter is the heart of any solar power system. Its primary job is to convert the Direct Current (DC) electricity generated by your solar panels into Alternating Current (AC) electricity. This is the standard form of power used by all your home appliances, from the television to the toaster.
Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT)
Modern solar inverters use a sophisticated technology called Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT). This technology constantly adjusts the electrical operating point of the solar panels to extract the maximum possible power from them.
In the UK's often cloudy and overcast conditions, MPPT is crucial for maximising energy collection throughout the day.
The Importance of Output Quality
A high-quality inverter for solar panels produces a pure sine wave output. This clean, stable power is identical to what you get from the grid, ensuring it can safely run sensitive electronics like laptops, modern boilers, and medical equipment without risk of damage.
Built-in Safety Features
Beyond power conversion, the inverter acts as a critical safety gateway. It provides essential protections, including overload, overvoltage, and short-circuit prevention, safeguarding both your connected appliances and the system itself.
Main Types of Solar Inverters
Understanding the different types of solar inverters is key to choosing the right setup for your needs.
|
Type of Inverter |
Description |
Pros |
Cons |
Best For |
|
String Inverters |
A single, central inverter connected to a "string" of solar panels wired in series. |
- Lower upfront cost. |
- Performance drops to the level of the weakest panel in the string. |
Large, unshaded rooftops with consistent sunlight throughout the day. |
|
Microinverters |
Small, individual inverters attached to each solar panel, converting DC to AC at the source. |
- Maximises output of each panel. |
- Higher upfront cost. |
Complex roofs with multiple angles, orientations, or partial shading. |
|
Hybrid Inverters |
Combines a standard solar inverter and battery inverter into one unit, powering the home and charging batteries directly. |
- Seamless integration with battery storage. |
- More expensive than string inverters. |
Homeowners planning both solar panels and battery storage from the outset. |
|
All-in-One Solar Generators (Portable Inverters) |
Portable units integrating an inverter, battery, and solar charge controller in one device. |
- Plug-and-play setup. |
- Smaller power capacity compared to permanent systems. |
Emergency backup power, off-grid cabins/workshops, portable power for travel or recreation. |
Efficiency Ratings and Why They Matter
The efficiency of a solar inverter measures how well it converts DC power to AC power. Most modern inverters boast efficiency ratings between 95% and 99%.
While a few percentage points may seem small, the difference adds up over the lifetime of the system. A higher efficiency rating means less energy is wasted as heat during the conversion process, resulting in more usable electricity to power your home and faster charging for your batteries.

Traditional vs. Modern Power Solutions: What's the Difference?
The choice of inverter often depends on your primary goal: reducing electricity bills through a permanent installation or ensuring power security with a flexible backup solution.
Traditional Grid-Tied Systems
Traditional solar setups, using string or microinverters, are complex and permanent fixtures. They are designed primarily to reduce your electricity bills by generating power for your home and, in some cases, feeding excess energy back to the grid. These systems require professional design, wiring diagrams, approval from your local Distribution Network Operator (DNO), and are not portable.
An Alternative: All-in-One Solar Generators
All-in-one solar generators offer a fundamentally different approach. They combine the inverter for solar panels, battery, and charge controller into a single, portable box. This integrated design makes them the ideal solution for emergency home backup, off-grid power, and ultimate simplicity. Their plug-and-play nature eliminates the need for electricians, complex wiring, or DNO approvals for backup purposes, providing immediate power security right out of the box.
How to Choose The Right Solar Inverter
Follow these three steps to find the perfect power solution for your needs.
Step 1: Define Your Primary Goal
First, identify what you need solar power for.
● Goal 1: Emergency Home Backup: Your priority is to keep essential appliances running during a power cut. This includes the refrigerator, internet router, lights, and any critical medical devices.
● Goal 2: Off-Grid Power: You need a reliable power source for a location without a grid connection, like a remote cabin, workshop, or allotment.
● Goal 3: Portability: You want to power tools on a job site, gear on a camping trip, or equipment at an outdoor event, far from any mains socket.
Step 2: Calculate Your Power Needs (Sizing)
Next, determine how much power you require. List the essential devices you want to run and find their wattage (usually printed on the device's label).
|
Appliance |
Typical Running Watts |
|
Refrigerator |
150 - 200W |
|
LED Lights (x4) |
40W |
|
WiFi Router |
10W |
|
Laptop |
60W |
|
Television (55") |
100W |
|
Sump Pump |
800 - 1000W |
|
Medical Device (e.g., CPAP) |
30 - 60W |
It's important to differentiate between running watts and surge watts. Appliances with motors, like refrigerators or pumps, require a much higher wattage for a few seconds to start up (surge) than they do to run continuously.
To find the battery capacity you need, multiply the total wattage of your devices by the number of hours you want to run them. This gives you a figure in Watt-hours (Wh). For example, running a 200W fridge and 10W router (210W total) for 8 hours requires 210W x 8h = 1680Wh of battery capacity.
● Jackery Solar Generator 2000 v2:
o 2042Wh capacity
o LiFePO4 battery with 4000-cycle lifespan
o <20ms UPS for seamless backup
o Recharges 0-100% in 1.8 hours via AC
o Ideal for running multiple essential appliances like a fridge, lights, and router for several hours.
● Jackery Solar Generator 3000v2:
o 3072Wh capacity
o LiFePO4 battery with 4000-cycle lifespan
o <20ms UPS for seamless backup
o Recharges 0-100% in 1.7 hours via AC
o Perfect for powering heavier loads like a microwave or for extended backup durations.
Step 3: Evaluate Key Features for Reliability and Longevity
Finally, look for features that ensure your investment is safe, reliable, and future-proof.
Battery Chemistry is Crucial
Always choose a system with a LiFePO4 (LFP) battery. These batteries are safer, more stable, and offer a significantly longer lifespan—often over 10 years of regular use—compared to older lithium-ion chemistries. This long-term reliability is vital for various applications, including enhancing home security with battery solar systems.
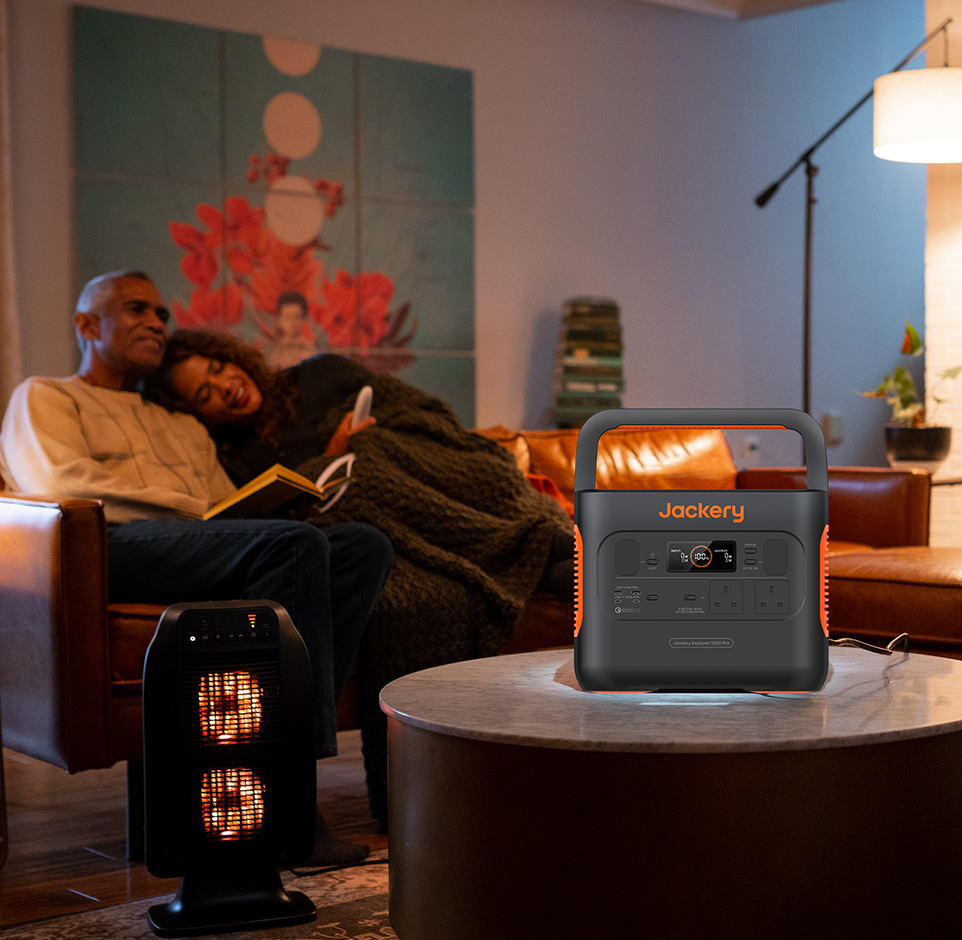
UPS Functionality for Uninterrupted Power
An Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) feature is essential for home backup. If the grid fails, a generator with a <20ms UPS transfer speed will switch to battery power so quickly that your connected devices won't even flicker, protecting sensitive electronics from shutting down.
Fast and Flexible Recharging
Look for a system that can be recharged quickly and conveniently. The ability to recharge from 0-100% in under two hours from a wall outlet ensures you are always prepared for an outage. Flexible solar charging is also key for true off-grid independence.
Smart Monitoring and Control
A companion smart app allows you to monitor power consumption, check battery status, and control outputs remotely from your phone. This gives you complete command over your power usage.
Expandability for Future-Proofing
Your power needs may grow over time. Choosing a system that allows you to add extra battery packs, like the Jackery Solar Generator 3000v2, which can be expanded to over 24kWh, ensures your solution can scale with your future requirements.
Take Control of Your Home's Energy Security
To secure your peace of mind, assess your home's essential appliance needs and compare them to the capabilities of a versatile solar generator. An investment in a unit like the Jackery Solar Generator 2000 v2 or 3000v2 is an investment in your family's comfort and security, today and for years to come. For a deeper comparison, explore this guide to backup generators.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How do solar generators perform during extended periods of cloudy UK weather, and what can I do to maximize their efficiency then?
A: During low sunlight, you can pre-charge the generator from a wall outlet before an expected outage. To maximise solar input, ensure panels are clean, angled directly towards the available sun, and consider using a generator with efficient MPPT technology.
Q2: What are the long-term cost savings of investing in a solar generator compared to relying solely on grid electricity and occasional generator rentals for outages?
A: A solar generator with a long-life LiFePO4 battery eliminates rental fees and provides free energy from the sun, offering a significant return on investment over its 10+ year lifespan. It also protects you from rising grid electricity prices for the power it generates.
Q3: Can a solar generator be integrated with existing smart home systems for automated power management during an outage?
A: While direct integration varies, you can use smart plugs with your solar generator to control which appliances receive power. This allows you to remotely manage and prioritise devices like fridges or routers during an outage.
Q4: What are the specific UK regulations or permits I need to be aware of if I plan to use a solar generator for partial home backup, especially if I want to connect it directly to my home's wiring via a transfer switch?
A: Using a portable solar generator to power devices via its outlets requires no special permits. However, connecting any generator to your home's wiring via a transfer switch must be done by a qualified electrician to comply with UK wiring regulations and DNO rules.
Q5: Beyond power outages, what are some creative or less obvious applications for a portable solar generator that could add value to a UK household?
A: You can use it to power electric garden tools, create an outdoor cinema with a projector, run a mobile office from your garden shed, or support community events. Its portability opens up a world of possibilities beyond just emergency backup.