How to DIY Home Battery Backup [Alternatives]
You and your family may be endangered during a blackout if you do not have a home backup power system. You can keep a standard fossil fuel generator on standby in a power loss. However, gas and diesel generators consume a lot of fuel, emit poisonous fumes, and are highly noisy – not to mention bad for the environment.
If you enjoy DIY projects, you can create your home battery backup system from the ground up. The procedure necessitates caution, attention to detail, and several critical components. Building a home battery backup system may be satisfying and cost-effective once you know how.
This page will guide you everything about DIY home battery backup, including the components needed, how to DIY home battery backup, mistakes to avoid, and what to consider when choosing the systems. The most important thing is the alternatives for home battery backup - Jackery Solar Generators, which combine solar panels and portable power stations to create the most convenient portable solar systems.
|
Products |
Images |
Capacity |
Rated / Peak Power |
Battery |
Size |
|
Solar Generator 2000 Plus |
 |
2-12 kWh |
3000W Rated, 6000W Peak |
LiFePO4 |
14.7x18.6x14.1in |
What Is Home Battery Backup?
In a world that is becoming increasingly digital, our dependence on electricity has never been greater. A constant and dependable power supply is indispensable, from running essential appliances to keeping us connected online.
However, the demand for home battery backup systems has increased as severe weather events and power disruptions become more frequent. These systems can provide energy independence, peace of mind, and even substantial energy bill savings.
A DIY home battery backup is a system that reserves energy generated by solar panels or the grid when power is available.
The stored energy can power your residence when electricity is unavailable or during peak demand periods when electricity prices are higher.
Why Do You Need A DIY Home Battery Backup?
Numerous catastrophes can occur these days due to extreme climate change, which will, in most cases, result in power outages. It would be best if you were prepared for power disruptions due to an aging infrastructure and more substantial natural disasters. It is optimal to have a home battery backup system for the following reasons:
Consistent Power Supply: Constructing a home battery backup system ensures a power supply even during catastrophic events and decaying infrastructure. Powering essentials like lights, the web, and the fridge can be maintained by drawing on the energy stored in batteries.
Increased Home Value: Installing a home battery backup system can increase the value of your home and make it more appealing to prospective buyers if you ever decide to sell.
Power Independence: Since batteries and solar panels can provide a portion of the required power, grid dependence will be reduced, thereby increasing the penetration of renewable energy.
Lower Electricity Bills: A backup battery can also be utilized during high-demand seasons, such as summer, to reduce electricity costs. The power required for running appliances can be divided between the grid, batteries, and solar panels. This results in reduced power consumption from the grid and, consequently, lower energy expenses.
What Are The Components of Home Battery Backup?
Constructing a home battery backup system takes more than just a battery and some cables. You must connect the battery to the electrical interface and ensure all system components are compatible.
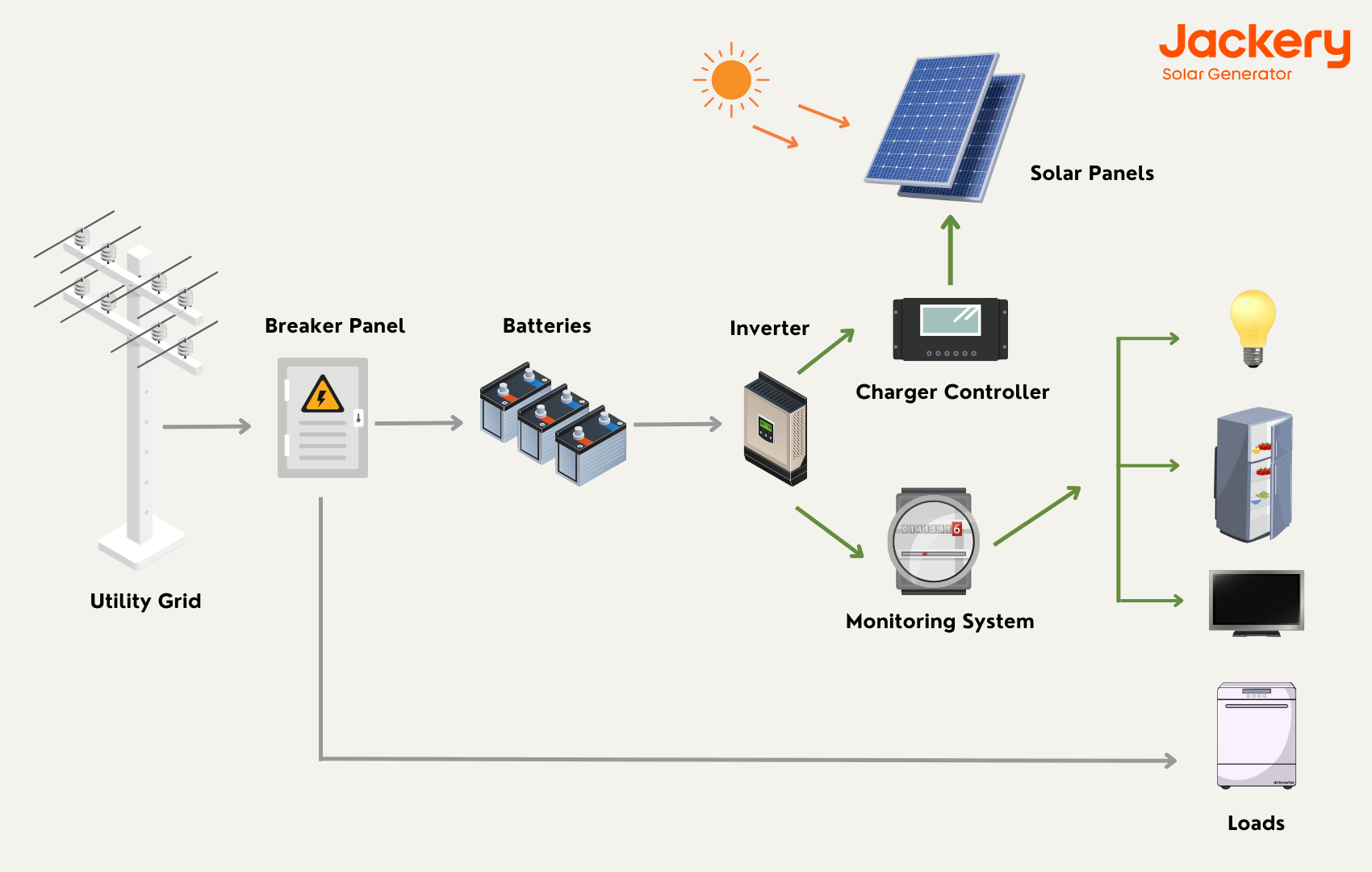
To construct an effective home battery backup system, you will need the following:
Battery: The battery is the most essential part of a home battery backup system. When electricity is available, it reserves the energy your solar panels, or the grid produces.
Inverter: The inverter converts the DC power stored in the battery to the AC power your domestic appliances require. To further guarantee that your battery is always ultimately charged and ready for use, it controls the flow of electricity between the battery, the solar panels, and the grid.
Charge Controller: Charge controllers are voltage and current regulators that prevent batteries from being overcharged. It regulates the current and voltage from the solar panels to the battery.
Monitoring: The monitoring system monitors energy consumption and battery health. It also provides information regarding the quantity of energy stored in the battery and the real-time energy consumption.
Wiring & Cable: The wires connect the battery to the inverter and charge controller to build a home battery backup system.
When there is available electricity, the battery backup system charges the battery. This can be accomplished in two ways: either through solar panels or the grid. If solar panels are installed, the battery backup system will power the battery with solar energy. If you lack solar panels or insufficient sunlight to charge the battery, the backup system will charge the battery from the utility.
How to DIY Your Home Battery Backup System?
This DIY home battery backup is ideal for prepper use and emergencies. During a power disruption, this system can power a refrigerator and a few lights for several hours.
Create a backup battery system for your residence or business. A battery backup system allows you to power essentials during a power outage. Using AGM or lithium batteries, this system is secure for indoor use; you can install it in a closet, office nook, or on a rolling cart to make it portable.
Step 1: Determine Your Power Consumption
Add the amperage of each device and appliance you wish to power or charge during a blackout to determine your household's energy consumption. You multiply the power in kW by the hours used per day, week, or month. You can use the following formula to compute your household's energy consumption:
kWh (kilo-watt-hours) = kW (kilowatt) x H (hours)
For instance, the TV has power of 120W, or 0.12 kW. They use it daily for 2 hours, so their daily electricity consumption is 0.24 kWh. To calculate your monthly consumption, multiply your daily consumption by the number of days, such as 30, to get your monthly consumption. Thus, your monthly consumption would be 7.2 kWh.
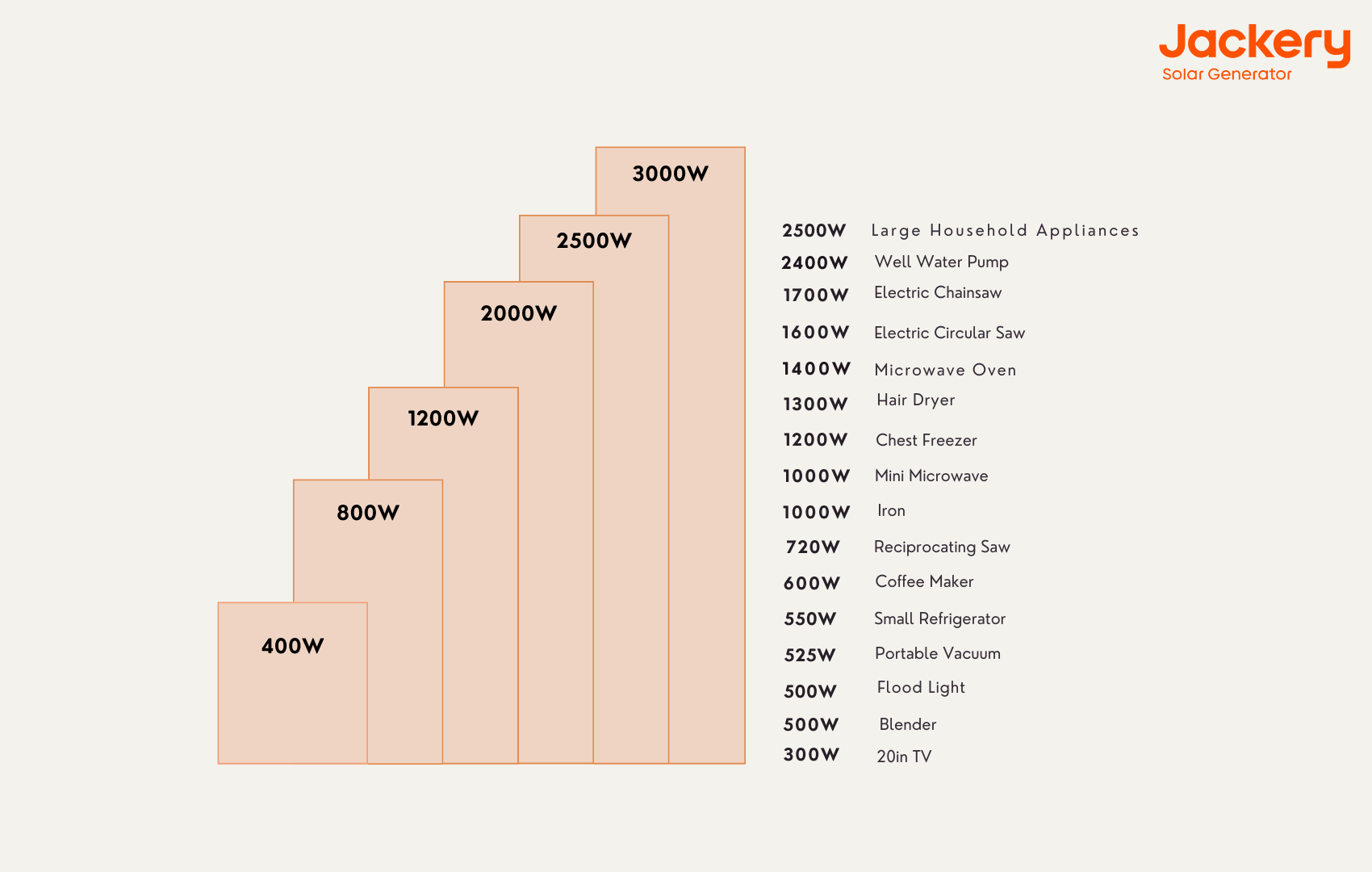
We have discussed how important it is to know how much energy your appliances consume. In light of this, we have compiled a list of the most common instruments and lighting, as well as the most common voltage range for these devices:
|
Appliances |
Running Watts |
Starting Watts |
|
Electric Blanket |
100-150W |
0 |
|
Laptops |
30-200W |
0 |
|
Cooler |
150-300W |
0 |
|
CPAP Machines |
30-60W |
0 |
|
Refrigerator |
300W |
1000W |
|
Air Conditioner |
900W |
1400W |
|
Heater |
1500W |
0 |
|
Vacuum Cleaner |
450-1000W |
0 |
|
Microwave |
1000W |
0 |
|
Washing Machine |
1150W |
2250W |
Step 2: Choose A Power Inverter
Selecting an inverter with a wattage rating that exceeds the power requirements of the devices in question is advisable. Calculating the total wattage of all the devices intended to be powered is also recommended. Typically, your appliances' labels will indicate the input wattage or amps.
Your household appliances are powered by alternating current (AC) electricity. Batteries, unfortunately, generate direct current (DC).
You cannot connect a battery directly to your residence's circuit board or appliances. The battery power must be converted into AC or household electricity.
Inverter refers to the device that converts DC power to AC electricity.
Choosing an inverter begins with figuring out how much electricity you need. An inverter will have a wattage rating, but you need to know the consumption requirements of the appliances and systems you wish to operate during a power outage. Otherwise, the inverter's wattage rating is mainly irrelevant.
Step 3: Select Batteries
Next, you must select your battery. You'll likely need multiple batteries for a residential battery backup power supply.
There are batteries with capacities ranging from 100Wh to 3kWh, which are suitable for powering large appliances. To determine how much power output and storage capacity you require, multiply the wattage requirements of the apparatus or devices you wish to power by how long you want to run them.
As mentioned before, operating a refrigerator with a power consumption of 300W over 5 hours would require a battery capable of delivering at least 300W of electricity and possessing a storage capacity of 1500 watt-hours (1.5 kWh).
Consider the charging and discharging times. The 12V 100Ah battery has a watt-hour capacity of 1200. However, only 50% is functional. If not, the battery will degrade rapidly.
Step 4: Need A Battery Charger
Next, you need a battery-charging component. With a charger and a regulator, batteries can be recharged without being overcharged. Ensure that your charger is compatible with your batteries to avoid damaging them.
You risk permanent damage and decreased performance if you repeatedly discharge or overcharge your batteries. You can maintain their optimum capacity and efficiency by measuring and regulating the charge your batteries receive between uses.
An ultimately charged battery will provide power for a longer duration during a blackout. You must purchase solar panels and a balance of system components if you're constructing a home battery backup system to ensure an off-grid energy supply. Ensure that the solar panels and battery are compatible with one another.
Step 5: Wire All Together
The initial component you will wire is the battery charger. Most charge controller instruction manuals will instruct you to attach the device to the batteries before calibrating it to the appropriate voltage for your batteries.
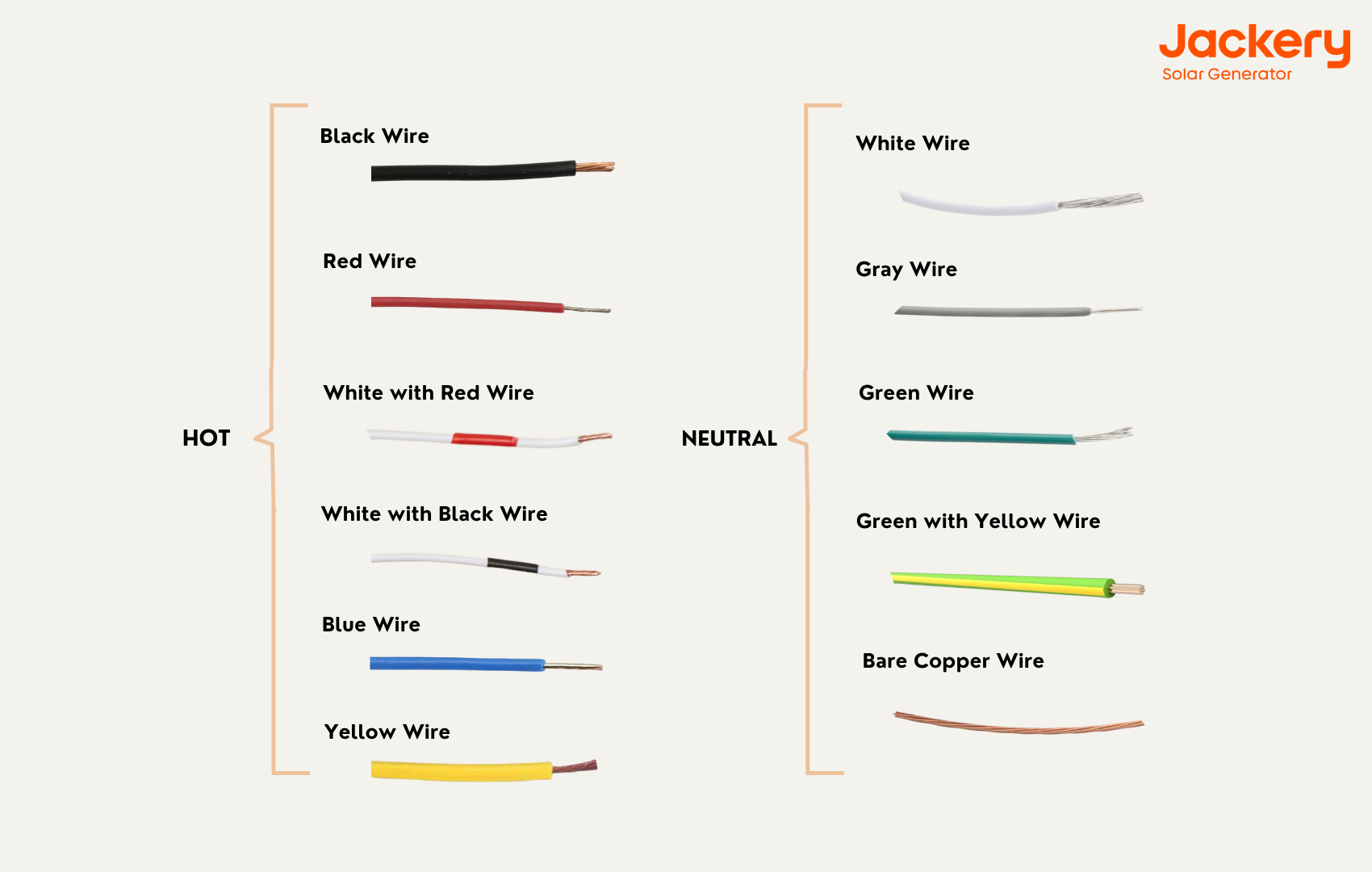

According to the laws, live wires may be represented by various hues. Black is the most common color for heated wires in residential circuits. Black conductors should not be utilized for anything other than electrical current.
Red is another standard color for a heated wire. In addition to the black wire, a red wire can be used as a live wire in 240-volt structures. White wires with red or black tape are also permitted as hot wires, albeit less frequently.
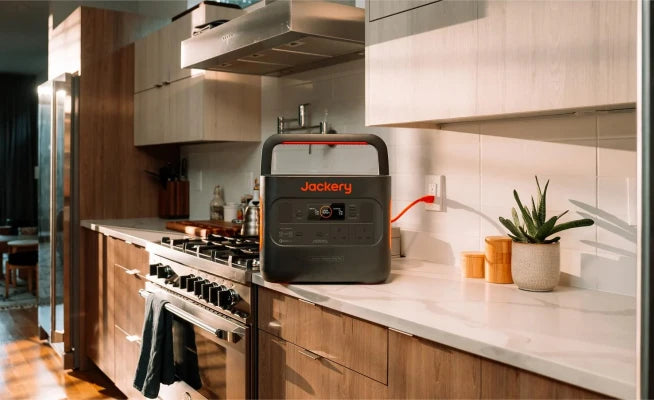
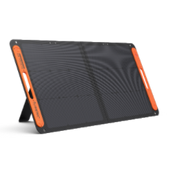
Home Battery Backup Alternatives: Jackery Solar Generators: Easy to Use and Reliable
A DIY home battery backup system requires multiple stages and the selection of numerous compatible components. There is considerable leeway for error. You could also purchase a plug-and-play solution.
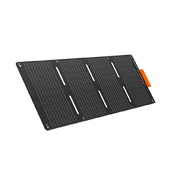
Jackery provides solutions to power and back up your household during a power outage. Alternatively, you can go completely off-grid with solar panels to achieve energy independence by utilizing Jackery Solar Generators, which consist of Portable Power Stations with Jackery Solar Panels placed in direct sunlight to convert solar energy into electrical power.
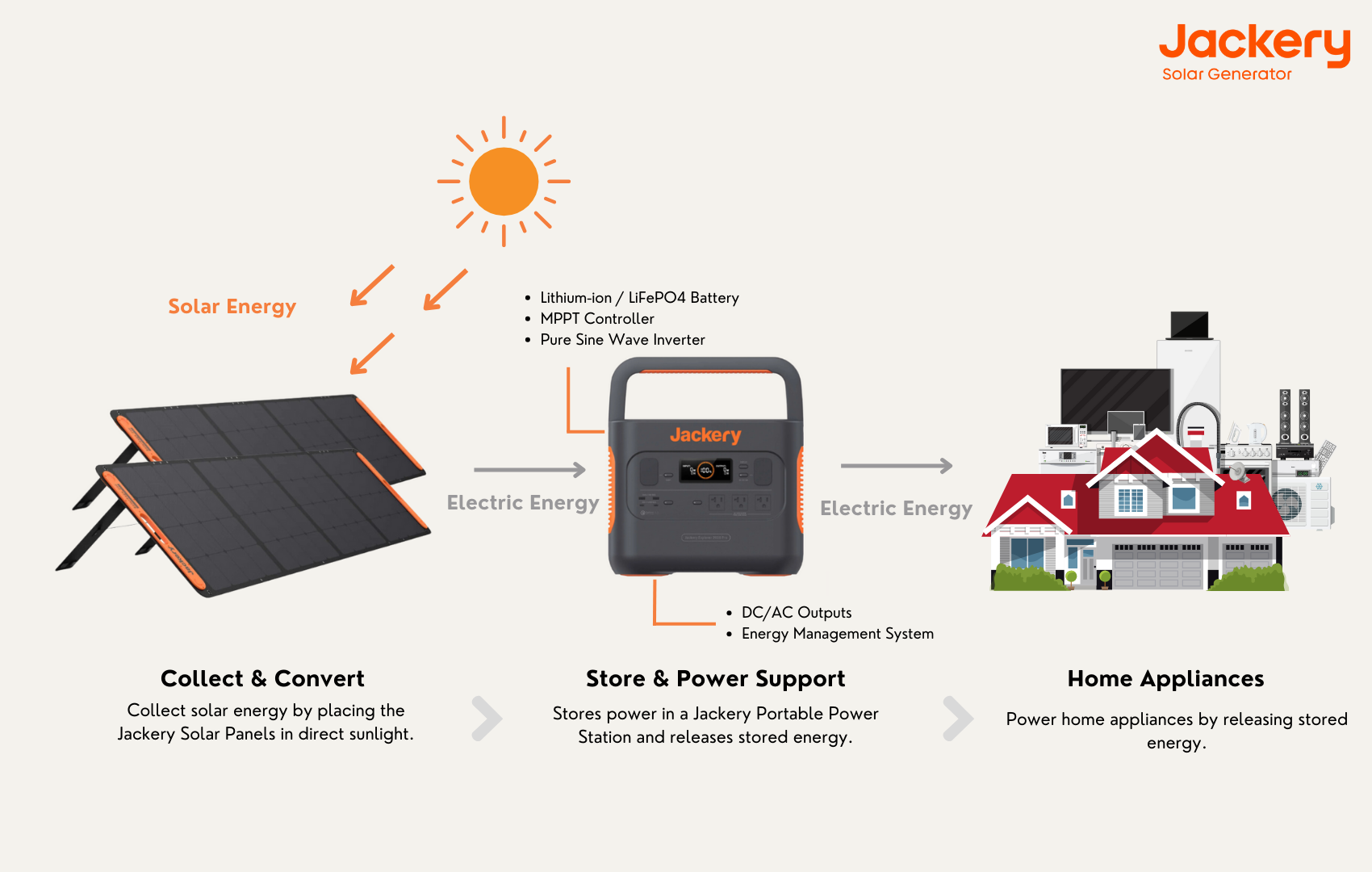
The Jackery Solar Generators are made and designed with user-friendliness in mind. The only requirement is to connect the Jackery Solar Panels to the Portable Power Stations. Solar panels can produce power when exposed to sunlight. The solar charging connectors enable the transmission of electrical energy to Portable Power Stations in a form that can power various appliances. The surplus electricity generated will be retained locally.
|
Specs |
Solar Generator 2000 Plus |
|
Capacity |
2042.8Wh |
|
Battery |
LFP (LiFePO4 battery) |
|
Life Cycles |
4000 cycles to 70%+ capacity |
|
Dimensions |
14.7x18.6x14.1in |
|
Using Temperature |
Charge Temperature:0~45°C (32~113 °F) Discharge Temperature:-10~45°C (14~113°F) |
|
Output Ports |
5*AC Output: 120V~ 60Hz, 20A Max, 120V~ 60Hz, 25A Max, 3000W Max, 6000W surge; 2*USB-A: Quick Charge 3.0, 18W Max; 2*USB-C: 100W Max, (5V, 12V, 9V, 15V, 20V up to 5A); 1*Carport: 12V⎓10A |
|
Working Hours |
Refrigerator(300-1000W): 1.6-5.4H Stove(1500W): 1.1H AC(900W): 1.8H CPAP(30-60W): 27.2-54.5H Washing Machine(1150W): 1.4H |
Jackery Solar Generators have capacities ranging from 240Wh to 12 kWh; to determine which Jackery Solar Generator is best for your household, use the following formula.
Working Hours = Jackery Portable Power Station Capacity x 0.85 / Appliance Wattage
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus
The Solar Generator 2000 Plus has an adjustable capacity between 2 and 12 kWh. With the addition of a battery cell and solar panels, a massive 12 kWh capacity is possible. It is suitable for emergency backup at home. An incredible two hours are required for a complete solar charge; power has become entirely autonomous, charging using solar energy.
The Explorer 2000 Plus portable power station takes solar charging to the next level with its 2 kWh capacity and up to 12 kWh of extended power. Ideal for short-term power disruptions, a single Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus power station can accommodate up to five add-on battery packs simultaneously, increasing capacity from 2 kWh to an impressive 12 kWh.

Connecting two Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus power stations increases capacity to a colossal 12 kWh, enough to power a home for an extended period.
The 2000 Plus's standby mode is so lengthy that it can hold a 50% charge for up to two years! Relax when you connect your appliances to our 2000 Plus! With a 20ms EPS, essential domestic appliances such as your refrigerator, oven, lighting system, and washing machine will continue to operate in the blink of an eye.
What Mistakes to Avoid for DIY Home Battery Backup?
If one opts to acquire separate components for a DIY home battery backup system, it is imperative to ascertain the compatibility of those elements. Failure to do so may result in the premature loss of the battery system, rendering it inoperable.
Likewise, it is imperative to procure components of high quality. Many individuals choose the do-it-yourself approach as a means of cost reduction. Nevertheless, it is advisable to maintain the quality of the components.
Mistake 1: Underestimate Power Needs
People will also need to pay more attention to their power requirements, so performing a thorough load calculation is essential before choosing the number and type of batteries to purchase.
Here are the most prevalent types of backup battery chemistry, ranked by efficiency:
- Deep cycle batteries
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP or LiFePO4) Batteries
- Lithium Ion (Li-ion) Batteries
- Nickel Cadmium (Ni-Cad) Batteries
- Lead Acid Batteries
However, the more influential the battery chemistry, the costlier the battery is likely to be. However, it would be a mistake only to consider upfront expenditures. Lead acid batteries must be replaced rapidly, whereas LiFePO4 batteries can last at least a decade.
Mistake 2: Incompatible Components
Selecting an inverter that aligns differently from the battery voltage or fails to meet the necessary wattage capacity can result in compatibility challenges and sub-optimal power conversion. Using incompatible inverters can impede electronic devices' proper functioning or even damage them.
Inadequate wiring, loose connections, or the utilization of inappropriate connectors can cause voltage dips, overheating, and potential fire dangers. Ensuring all connections are securely fastened, well insulated, and suitable for the prevailing electrical load is imperative.
Mistake 3: Neglect Safety Concerns
Ensuring safety is of utmost importance when engaging in tasks using electricity. Neglecting safety protocols, such as deactivating the system and donning suitable protective equipment, might result in electrical mishaps and bodily harm.
It is imperative to engage in the practice of consulting instruction manuals and seeking assistance when faced with uncertainty about appropriate actions. Conducting a thorough study to mitigate the potential harm to your battery backup system is advisable. Although it is possible to install a DIY home battery backup system independently, allocating sufficient time to familiarize oneself with the process and ensure a comprehensive understanding of the task is crucial.
How to Choose The Home Battery Backup System?
When selecting the most effective home battery backup system, it is essential to consider various technical factors, such as peak, start, operating voltage, and amperage. These permanent installations must be capable of managing the daily electrical load of all household appliances.
Choosing a system with inadequate capacity can cause electrical wiring problems while selecting a system with excess capacity ensures smooth operation and allows for future expansion as power requirements change. Pricing and installation expenses are also crucial considerations when making a choice.

Several factors determine a home's optimal battery backup, including power needs, budget, and intended system lifespan. Lithium batteries are one of the best options available on the market due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and exceptional depth of discharge.
They combine performance, efficiency, and dependability, making them an excellent option for residential backup systems. Jackery Solar Generators, for instance, are constructed with lithium-ion and LiFePO4 batteries to store more energy and extend their lifespans.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, installing a DIY home battery backup is crucial for ensuring a continuous power supply and protecting the comfort and functionality of your home during power outages. This is especially important in regions prone to natural disasters or unreliable grid power.
By grasping the essential components of the home backup system, you will be able to complete the task without assistance. However, DIY home battery backup has some mistakes so a Jackery Solar Generator may be the best option for home emergencies with higher capacities.