The rapid expansion of digital infrastructure needed to power Artificial Intelligence is placing immense strain on the UK’s National Grid. As tech giants build more facilities, homeowners are right to worry about grid reliability and the possibility that they are indirectly subsidizing the energy demands of global corporations. To understand where your monthly statement is heading, you need to understand the relationship between AI and energy consumption.
What Is Data Center Energy Consumption?
Data center energy consumption refers to the total electricity needed to run servers, storage, and networking equipment. However, it isn’t just about powering the computers; a massive amount of energy is required for cooling systems to prevent this sensitive hardware from overheating.
Why Is This Relevant to Consumers?
When these facilities draw huge amounts of power, they stress the wider energy network. This high demand influences wholesale electricity prices and forces the National Grid to make expensive infrastructure upgrades to maintain stability. For the average consumer, this is crucial. As industrial demand alters the balance of supply and demand, these systemic costs can trickle down to household bills, potentially leading to higher standing charges or unit rates in the near future.
Why AI Workloads Are Energy Hogs
AI operations differ significantly from standard cloud computing. The specific nature of machine learning creates distinct energy profiles that are far more demanding than hosting a website or streaming a video.
- Computational Intensity: Unlike fluctuating internet traffic, training AI keeps thousands of GPUs at max capacity for weeks, causing sustained power drain.
- Always-On Inference: Serving millions of daily interactions creates a high energy baseline, as every query triggers complex processing rather than a simple database lookup.
- Hardware Density: Packing specialized chips tightly generates massive heat per square metre, forcing data centers to spend significantly more energy on cooling.
- Generic Inefficiency: Using massive LLMs for minor tasks is "computational overkill," activating billions of parameters to answer simple questions where traditional software would use a fraction of the power.
How Data Centers Impact UK Bills
The connection between a server farm in Slough and a household bill in Manchester is not immediately obvious. However, several economic and physical mechanisms transfer the costs of high industrial demand to the general populace.
|
Economic Mechanism |
How It Works |
Impact on Your Bill |
|
Wholesale Price Inflation |
High demand raises the market clearing price (the cost of the most expensive generator needed). |
Since the price cap is based on wholesale costs, this pushes up retail tariffs for everyone. |
|
Socialised Infrastructure |
The National Grid and DNOs must reinforce substations and lines to handle massive server loads. |
Under UK regulations, these upgrade costs are spread across all ratepayers, appearing as increased network charges. |
|
Capacity Market Costs |
To ensure the lights stay on, the grid pays generators to keep backup power ready for high-load periods. |
Data centres increase the total backup capacity required; the cost of this "safety margin" is passed down to consumers. |
|
Peak Timing Pressure |
Data centres run 24/7, overlapping with household peak hours (4 pm–7 pm). |
This forces the grid to fire up expensive "peaking" power plants, raising the overall cost of electricity. |
|
Location Constraints |
Clusters in areas like Slough or the M4 corridor put immense strain on local grids. |
Localised constraints can delay new housing or renewable projects, indirectly increasing system costs. |
Direct vs. Indirect Impact on Your Wallet
Does Personal Usage Cost More?
Using AI tools on your personal device has a negligible impact on your personal electricity meter. Whether you are drafting an email with a chatbot or generating an image, the power draw on your laptop or phone is minimal because the heavy processing happens remotely.
Where Do the Indirect Costs Come From?
Indirect costs come from system-level effects passed down via standing charges and unit rates. As the grid requires more investment to support AI data center consumption, the "network costs" portion of your energy bill—which makes up a significant percentage of the total—may rise.
How Should You Analyze Your Bill?
Analyzing your bill requires looking beyond the meter to the wider grid environment if you notice recent hikes. These increases are likely due to broader wholesale market shifts and network upgrades rather than your specific usage habits, which helps explain why is my electric bill so high even when personal consumption remains flat.
The UK Context: Planning and Policy
The UK grid is currently facing significant bottlenecks. The queue for grid connections is long, and the addition of gigawatt-scale data centres exacerbates this congestion.
Are There Grid Constraints?
Grid constraints occur when high-demand connections delay the integration of renewable energy sources. If grid capacity is used up by data centres, wind and solar farms may face delays in connecting to the network, slowing the transition to cheaper, greener energy.
What Regulatory Levers Exist?
Regulatory levers include "connection charges" determined by local authorities and DNOs. While the connector historically paid for immediate work, deep reinforcement costs were shared. Ofgem is constantly reviewing these charging arrangements to ensure fairness in cost allocation.
What Is the Current Policy Debate?
The current policy debate focuses on whether developers or consumers should bear the full cost of reinforcement. If developers are not required to fund the wider grid impact of their facilities, the default mechanism socialises these costs onto household bills.
Energy Independence and Backup Solutions
As grid strain increases, achieving a degree of energy independence becomes a prudent financial and security strategy.

Is Solar Integration Worth It?
Solar integration is worth the investment because domestic installations reduce reliance on the grid. By generating your own power, you hedge against wholesale price volatility and network cost increases, ensuring every kilowatt-hour you generate is one you do not have to buy at market rates.
How Does Battery Storage Help?
Home batteries help by allowing users to store cheap off-peak energy for use during expensive peaks. This arbitrage strategy is particularly effective if grid volatility increases due to rising industrial demand.
Why Consider Portable Solutions?
Portable solutions offer flexibility for renters or those needing specific backup capabilities. These units provide security against local outages caused by grid strain and allow for off-grid energy usage.
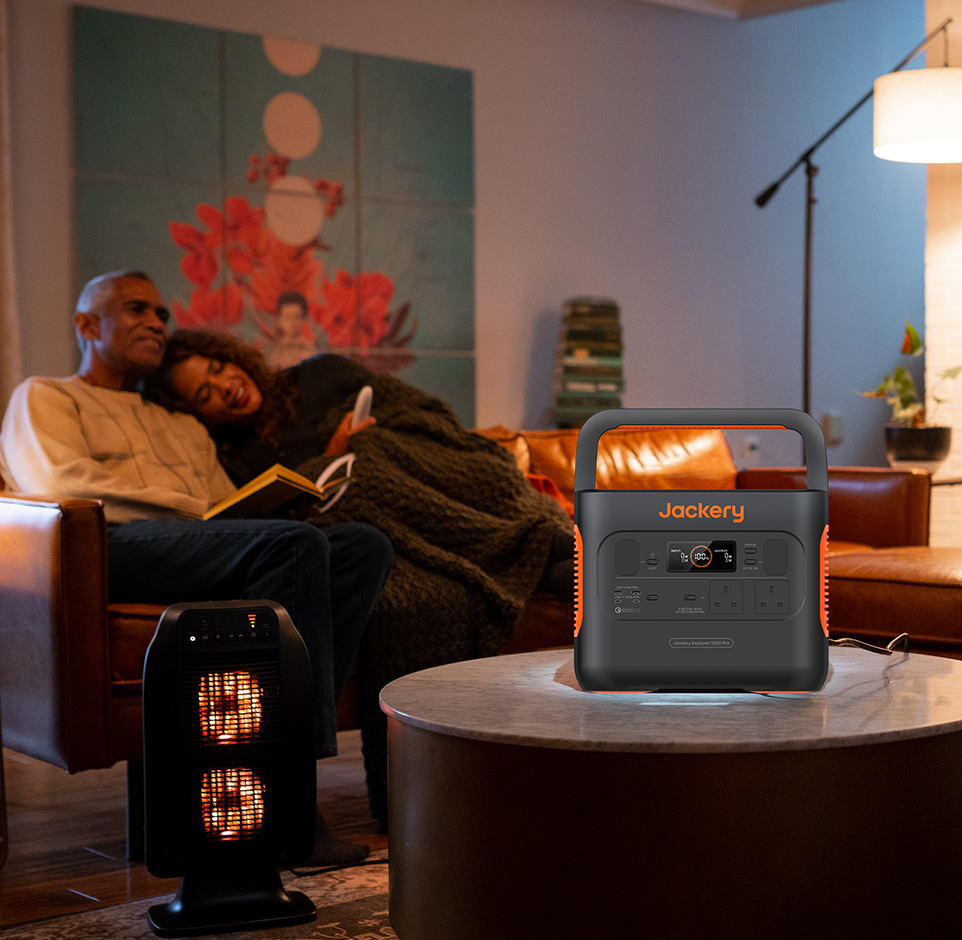
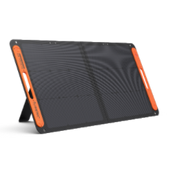
Example Option: Jackery Explorer 1000 v2 Portable Power Station
The Jackery Explorer 1000 v2 serves as an illustrative solution for household energy resilience.
- Capacity: The Jackery Explorer 1000 v2 offers 1070Wh capacity, sufficient to back up essential devices like routers, lights, and computers during local outages.
- Output: This portable power station delivers 1500W output (3000W surge), capable of running 93% of home appliances, including high-draw items like fridges or kettles.
- Longevity: The unit uses LiFePO4 battery chemistry for 4,000 charge cycles, providing approximately 10 years of daily use.
- Emergency Use: Jackery Explorer 1000 v2 features Emergency Super Charging to fully recharge in 1 hour via a standard wall outlet, ensuring readiness for sudden grid instability.
Use Case: This unit acts as a buffer against grid unreliability, keeping essential home office equipment or medical devices running regardless of external supply issues.
Community and Regulatory Action
Individual efficiency is vital, but collective action drives systemic change. Households have a voice in how the energy landscape evolves.
How Can You Engage Civically?
Engaging civically involves participating in local planning consultations for proposed data facilities. Local councils often hold public comment periods where residents can raise concerns about infrastructure strain and energy requirements.
Why Request Transparency?
Requesting transparency ensures developers fund necessary upgrades through "Grid Impact Assessments." Demanding this clarity ensures that the costs of reinforcing the local network are borne by the commercial entities profiting from it, rather than the community.
How Can Advocacy Help?
Advocacy helps by supporting policies that prevent the socialisation of private infrastructure costs onto household bills. Advocacy groups and consumer watchdogs are instrumental in pressuring regulators to protect the average electric bill for a 2-person household in the UK from unfair hikes.
Can Communities Benefit?
Communities can benefit by pushing for agreements where waste heat is captured. Modern data centres generate immense heat, and residents can demand this be used for district heating networks, providing cheap, low-carbon warmth to local homes.
Conclusion
The rapid rise of AI offers technological marvels but brings tangible challenges to the UK energy grid. While your individual use of AI tools is inexpensive, the data center energy consumption required to support this ecosystem drives systemic costs that can trickle down to household bills.
The outlook for your energy costs depends heavily on how effectively the UK regulates grid upgrades and cost allocation in the coming years. However, you are not powerless. Through energy efficiency, load shifting, and investing in backup solutions like solar generators, you can build resilience against market volatility. Active engagement in local planning further ensures that the cost of the AI revolution is not unfairly placed on the consumer.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much energy does a single AI query consume?
A single AI query can consume up to 10 times more electricity than a standard Google search. This is because the inference process requires activating massive neural networks for every individual response.
Are there greener alternatives for AI data centers?
Yes, many operators are locating facilities in regions with abundant renewable energy, such as the Nordics. Additionally, innovations in liquid cooling and waste heat recovery are significantly improving the energy efficiency of these sites.
Can AI itself optimize data center energy usage?
AI is increasingly used to manage cooling systems and server loads within data centres. By predicting demand spikes and adjusting cooling in real-time, AI can reduce facility energy consumption by up to 40%.