How much electricity does your television actually use? With energy prices fluctuating, understanding TV wattage has become critical for UK homeowners. Whether you have an LED, OLED, LCD, or plasma screen, the wattage of your television directly affects your electricity consumption.
This article investigates how many watts a TV uses based on screen size and technology, provides simple formulas for estimating power expenses, and recommends practical energy-saving tips. Learn about the average power consumption of various TV sizes and how energy-efficient models and smart watching habits can help you save money and power.
|
Key Takeaways: |
|
How Many Watts Does a TV Use?
TV wattage varies by model, size, and special features. The average current TV wattage is between 50 and 200W. This is a crucial average to keep in mind. Before we go into the formula for determining TV energy use, we must first define "watts".
What Does "Watts" Really Mean
Wattage is frequently used as the unit of measurement when determining how much electricity a television requires.
Watts (W): Determine how much electricity the TV draws at any one time.
Kilowatt-hours (kWh): Determine how much energy is spent over time.
Although watts may appear on various devices, like your television, kilowatt-hours are what you will see on your electricity bills, so it is critical to understand how they relate.
Do TVs Use a Lot of Electricity?
Whether a TV uses "a lot" of electricity depends on its type, size, and usage habits. On average:
A basic LED TV may consume approximately 100 kWh per year if used for 4 hours per day.
Larger or older TVs, particularly plasma models, can consume much more power, often doubling or tripling that of a regular LED TV.
TVs typically consume less electricity than refrigerators or air conditioners, but they can still add to energy bills over time, mainly if larger, higher-definition versions are used regularly.

Calculating Energy Costs: How Much Power Does A TV Use?
The average television viewing time for adults in the United States has gradually declined, with recent estimates indicating that people now watch about 3 hours of television each day, for a television with an average power consumption of 100 watts, 1.5 hours of viewing per day results in approximately 1.05 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity consumed weekly, or 4.55 kWh monthly and 54.6 kWh annually.
Increasing the viewing period to three hours per day would increase electricity use by 2.1 kWh per week, 9.1 kWh per month, and 109.2 kWh per year. If the TV is utilised for 4.5 hours each day, the weekly energy usage rises to 3.15 kWh, for a total of 13.65 kWh monthly and 163.8 kWh annually.
Different television models have varying wattage ratings, resulting in different annual electricity consumption numbers. For example, if a TV is used for three hours every day, the annual energy consumption based on wattage is as follows:
Estimated Annual Electricity Use by TV Power Rating
|
Rated Power (Watts) |
Yearly Energy Use (kWh) — Based on ~1,095 Hours of Viewing |
|
50 W |
54.75 kWh |
|
75 W |
82.13 kWh |
|
100 W |
109.5 kWh |
|
125 W |
136.9 kWh |
|
150 W |
164.25 kWh |
|
175 W |
191.63 kWh |
|
200 W |
218 kWh |
|
225 W |
244.38 kWh |
|
250 W |
270.75 kWh |
When estimating energy expenditures, it is crucial to consider not only a television's wattage but also its energy efficiency. The ENERGY STAR program ranks televisions by energy efficiency, with higher ratings indicating more efficient models.
How to Calculate the Energy Use of Your TV?
You may estimate your TV's energy consumption using this easy formula:
kWh = (TV Wattage × Hours Used Per Day) ÷ 1000
Let's use some numbers as an example. A 100-watt television running for 5 hours uses:
100 W × 5 hours ÷ 1000 equals 0.5 kWh.
Multiplying 0.5 kWh each day by 30 days yields an average monthly usage of 15 kWh.
Typical Wattage by TV Types
The sort of television you own will influence its power consumption, with some requiring substantially less than others. The chart below illustrates common TV kinds and their wattage ranges.
|
Type of TV |
Average Wattage Range |
|
LED TV |
50-100 W |
|
OLED TV |
60-3500 W |
|
LCD TV |
70-200 W |
|
Plasma TV |
100-500W |
How Many Watts Does a 70-Inch TV Use?
A 70-inch television (or close variant, e.g. 69.5″) is among the largest models commonly sold in the UK, and its power draw is accordingly substantial. An LED or LCD television with a screen size of 70 inches (approximately 69.5 inches) will typically consume 170 to 200 watts of power (or more when operating in high dynamic range or high brightness mode).
How Many Watts Does a 65-Inch TV Use?
On average, a 65-inch television uses 200-250 watts of power. This indicates that if you watch it for three hours per day, your annual energy consumption will be approximately 218-273.75 kWh. However, as previously said, this may vary based on the model and its energy efficiency rating.
Newer TV models are more energy efficient than older ones. This is due to technological improvements that have made energy management and conservation more efficient.
How Many Watts Does a 55-Inch TV Use?
The power consumption of a 55-inch television varies greatly depending on the display technology. A 55-inch LCD TV typically requires around 180 watts, but an LED TV consumes approximately 80 watts. An OLED TV uses roughly 98 watts, whereas a plasma TV requires approximately 370 watts.
When calculating the wattage of a 55-inch TV, factors such as brightness settings, usage patterns, and unique features must be considered. For example, if the TV has a greater brightness level or other features such as HDR (High Dynamic Range), it may use more power.
Furthermore, while watching content in different modes or playing games may use more energy than regular viewing, power consumption rates can vary across manufacturers and models.
How Many Watts Does a 50-Inch TV Use?
When estimating how many watts a 50-inch television might draw, there is naturally a variation depending on the display technology (LED, LCD, OLED, etc.), the brightness settings, and efficiency.
A typical 50-inch LED/LCD TV uses 70- 120W during normal viewing. Under brighter settings or less efficient models, it could go higher. To estimate cost, multiply that by the hours used per day, then convert to kWh.
How Many Watts Does a 40-Inch TV Use?
The power required by a 40-inch TV varies by model. The approximate power usage for several types of 40-inch televisions is as follows:
|
40-Inch TV |
Wattage |
|
LCD TV |
100W |
|
LED TV |
50W |
|
OLED TV |
72W |
|
Plasma TV |
200 W |
|
CRT Television |
N/A |
Most new 40-inch TVs are energy-efficient and might use fewer watts than larger or older ones. However, it is still necessary to consult the manufacturer's specs to discover the precise wattage consumption of a particular TV model.
How Many Watts Does a 32-Inch TV Use?
A 32-inch TV uses typically 70 watts for an LCD, 41 watts for an LED, and 160 watts for a plasma. It is crucial to note that energy usage varies by manufacturer and model, so examining the energy efficiency rating will help you make a more informed decision when choosing a television.
How Many Watts Does a 24-Inch TV Use?
Smaller TVs draw considerably less power. In regular viewing mode, a 24-inch LED or LCD TV may use between 20 and 40 watts. Because power grows roughly with screen area (and illumination requirements), smaller screens consume substantially less electricity.
How Many Watts Per Hour Does a Television Use?
The wattage required by a TV is typically expressed in watts per hour, though it should be noted that this generally refers to the average power consumed while the TV is on. Most modern televisions have an active mode power range of 50 to 300 watts, depending on size and technology.
For example, an LCD TV may consume 70-80 watts, whereas an LED TV can consume 30 to 150 watts. To accurately assess energy consumption, consider both the average usage length and the wattage. For example, if a TV uses 100 watts and is viewed for 5 hours, it will spend 500 watt-hours (0.5 kilowatt-hours) in that time.

How Much Does It Cost to Power a TV?
The total on your electricity bill is a flat number; it does not break down how much each gadget contributes. The table below shows the cost of running a TV for a month or a year, based on typical UK electricity prices.
|
Region / Scenario |
Typical Electricity Rate* |
Approx. TV Cost per Month |
Approx. TV Cost per Year |
|
UK average (2025) |
~26.35 p per kWh (variable rate) |
~£2.57 |
~£30.80 |
|
High-usage / premium rate |
~30 p per kWh |
~£2.92 |
~£35.00 |
|
Low-rate / off-peak |
~22 p per kWh |
~£2.14 |
~£25.70 |
Based on the October–December 2025 electricity price cap, which sets the unit rate at around 26.35 p/kWh for domestic users.
In the United Kingdom, most current TVs have a wide range of power needs based on size and technology. Typical TVs utilise between 30 and 300 W, depending on model, display type, and usage.
For example, using a 120 W LCD panel for an 8-hour session may cost around 21.5 p each day, or approximately £7.85 per month, based on 26.35 p per kWh.
Newer high-efficiency LED and OLED sets use less energy for the same performance. Still, in some circumstances -- particularly with large luxury OLED/QLED models -- power consumption can be higher than that of a typical LED set. In many cases, current televisions use less energy per unit of image quality than earlier plasma versions.
Below is a table showing monthly and annual costs for various TV power draws and screen technologies.
|
Screen / Technology |
Typical Power Draw |
Cost per Hour† |
Cost per Day (4 h use) |
Cost per Month (30 days) |
Cost per Year (365 days) |
|
Small LED / LCD (30–50 W) |
~40 W |
~1.03 p |
~4.1 p |
~£1.24 |
~£15.07 |
|
Medium LED / LCD (80–120 W) |
~100 W |
~2.57 p |
~10.3 p |
~£3.08 |
~£37.50 |
|
Large LED / LCD (150–200 W) |
~160 W |
~4.12 p |
~16.5 p |
~£4.95 |
~£60.68 |
|
OLED / QLED (mid to large) |
~120–180 W |
~3.09–4.63 p |
~12.4–18.5 p |
~£3.72–£5.56 |
~£45.38–£67.50 |
|
Older Plasma / High-power sets |
~250–300 W |
~6.43–7.72 p |
~25.7–30.9 p |
~£7.71–£9.27 |
~£94.10–£113.60 |
Cost per hour = (Wattage ÷ 1,000) × 25.73 p
What Affects the Power Consumption of TVs?
Now that you understand the basic average, let's take a closer look at the aspects that influence television power consumption:

TV Type, Size and Screen Resolution
Different types and sizes of televisions have varying power consumption values.
For example, a 32-inch LED television typically requires 30 to 55 watts; however, an OLED television may demand slightly more, about 55 to 60 watts. In contrast, a 32-inch LCD TV typically requires more electricity, ranging from 50 to 85 watts. However, older 32-inch CRT televisions are the most power-hungry, consuming between 150 and 200 watts and averaging around 170 watts.
A 55-inch LED TV, on the other hand, typically consumes between 60 and 90 watts, while an 8K OLED TV can consume up to 350 watts. An older 55-inch CRT TV can use up to 300 watts, although the average is around 280 watts.
The screen resolution also significantly affects power consumption. Higher resolutions typically demand more power to generate a crisp image. For example, a Full HD (1080p) TV consumes less energy than a 4K or 8K TV of the same size.
LED Televisions (50-100W): These are the most widespread on the market and, in most cases, the most energy efficient. They consume less electricity, often 50 to 100 watts, thanks to their energy-efficient LED (Light Emitting Diode) backlighting.
LCD Televisions (70-200 W): LCD TVs are older than LED models and use a different backlighting system that consumes more energy. They should draw between 70 and 200 watts, depending on the type and settings.
Plasma Televisions (100-500 W): They are noted for their high contrast and colour accuracy, but their gas-based lighting technique requires substantially more electricity, ranging from 100 to 500 watts. It is less common in modern houses.
OLED/QLED TVs (60-350 W): These latest models offer excellent image quality because OLEDs use separate light-emitting diodes for each pixel. They typically consume between 60 and 350 watts, making them slightly more efficient than plasma but more power hungry than LEDs.
CRT Televisions (100-400 watts): These older types (Cathode Ray Tubes) are large and power-hungry. They were ubiquitous before flat-screen TVs took over and ranged in power from 100 to 400 watts, depending on size.
Screen Size: Larger TVs consume more power because it takes more energy to illuminate a larger display. Here's a quick reference for the TV power draw of various screen sizes:
Typical Power Consumption by TV Type and Screen Size
|
Screen Size |
LED Display |
LCD Display |
Plasma Display |
OLED / QLED Display |
|
24" |
35 W |
50 W |
— |
— |
|
30" |
38 W |
60 W |
150 W |
— |
|
32" |
42 W |
70 W |
160 W |
— |
|
37" |
44 W |
80 W |
180 W |
66 W |
|
40" |
50 W |
100 W |
200 W |
72 W |
|
42" |
58 W |
120 W |
220 W |
75 W |
|
50" |
72 W |
150 W |
300 W |
90 W |
|
55" |
80 W |
180 W |
370 W |
98 W |
|
60" |
88 W |
200 W |
500 W |
108 W |
Brightness Settings
Increasing brightness feels cinematic, but it also increases energy use. Most televisions default to "Vivid" or "Dynamic" settings, which maximise brightness. It can waste 20 to 40% more power than a lower brightness setting.
Many new televisions also include an "eco" or "energy-saving" mode that automatically adjusts brightness based on ambient light, reducing energy use.
Usage Patterns
The frequency and duration of your TV viewing can significantly impact your overall energy use. If you leave your television on all day, even when you aren't viewing it, your energy bill will inevitably rise. Similarly, binge-watching for hours on end will increase power use.
A regular TV may be used for an average of 4-6 hours per day, resulting in an energy consumption of 200 to 600 Wh per day, depending on the model and settings. However, if you watch in small bursts or do not watch at all, you will undoubtedly use less energy.
Standby Mode Consumption
Even when "off," many televisions continue to consume power for features such as instant-on or updates (known as vampire power). Modern televisions consume approximately 0.5-5 watts in standby mode. While this appears insignificant, it adds up over time.
For example, if your TV uses 3 watts in standby mode and stays there for 24 hours a day for a month, it will consume around 2.16 kWh.
Energy Efficiency Ratings
When shopping for a new television, choosing a model with a higher energy efficiency rating means it will use less electricity to deliver the same level of performance. In the UK, TVs are rated from A (most efficient) to G (least efficient).
An A-rated television can save you a significant amount on your electricity bills over its lifetime compared to a D-rated model. ENERGY STAR®-certified televisions — often found in imported models — are also excellent options for improved energy efficiency.
How Can You Check Your TV’s Power Consumption?
It's easier than you think to figure out how much electricity your TV uses. One of the simplest ways to find out is to look at the label on the back of your TV or read the user manual. Manufacturers typically specify the amount of electricity utilised in watts or amps.
Another successful approach is to use a power cadence, such as the Kill-A-Watt. Plug your television into the cadence, and it will display exactly how much power it is consuming. This is an excellent technique for determining how much electricity your television actually uses while in use. This tool will provide a precise response to the question, "How many Watts does a TV use in normal conditions?"
You can also learn about the importance of power commodities by visiting the manufacturer's website. Brands usually release comprehensive specifications, including average and peak power consumption. However, use the following formula: watts are calculated by multiplying the voltage and amperes to determine the commodity quickly.
TV Power Consumption When Off
When a television is turned off, it typically enters standby mode to facilitate a speedy power-up and preserve specific settings. On average, the most recent televisions consume approximately 1.3 watts of power while in standby mode.
However, the power consumption of televisions in standby mode can range from 0.5W to 3W. This range is due to different technologies and television sizes available on the market, which result in varying levels of power consumption. Some more advanced models may consume less power in standby mode due to energy-saving features and efficient design.
Tips for Reducing TV Power Consumption
Reducing your television's power consumption not only lowers your electricity bills but also contributes to a more sustainable home. Here are some basic but effective ways to reduce the energy your television uses.

Turn off the Television While Not in Use
Turning off your television when you are not interested in watching it is one of the most popular and straightforward ways to reduce the energy you consume. As long as it is in standby mode, it will continue to drain power; therefore, you should be sure to turn it off completely.
Change the Brightness and Contrast Settings
By default, many televisions have brightness and contrast settings set to high levels. By lowering these settings, you can help save energy without sacrificing picture quality.
Implement Energy-Saving Features
A significant number of contemporary televisions come equipped with built-in energy-saving features, such as sleep timers, eco-mode settings, and automated brightness control. Ensure these functions are activated to reduce your power use.
Upgrade to an Energy-Efficient Television
If you have an older television, consider upgrading to a newer, more energy-efficient model. When shopping for a television, look for models with the ENERGY STAR designation, as they use significantly less electricity and help you save money on your monthly energy costs.
Make Use of a Portable Power Station
Using a portable power station can be a practical and energy-efficient way to power your television, especially during power outages or in areas with an unstable electricity supply. These devices store energy from the grid or solar panels and may power your TV, lights, and other electronics without requiring mains power. The Jackery Explorer 1000 v2 and Jackery Explorer 500 v2 are outstanding examples of portable power solutions that may be used both indoors and outdoors.
Can the Jackery Portable Power Station Run a TV?
A television can, in fact, be powered by a generator. On the other hand, it is essential to ensure the generator's capacity is adequate for the solar-powered television and any other appliances you intend to use simultaneously.
Jackery can power speakers, projectors, and other electronic entertainment devices. Jackery can also power televisions. A variety of TVs can be powered for a considerable time by Jackery Portable Power Stations, which are vital home backup power solutions.
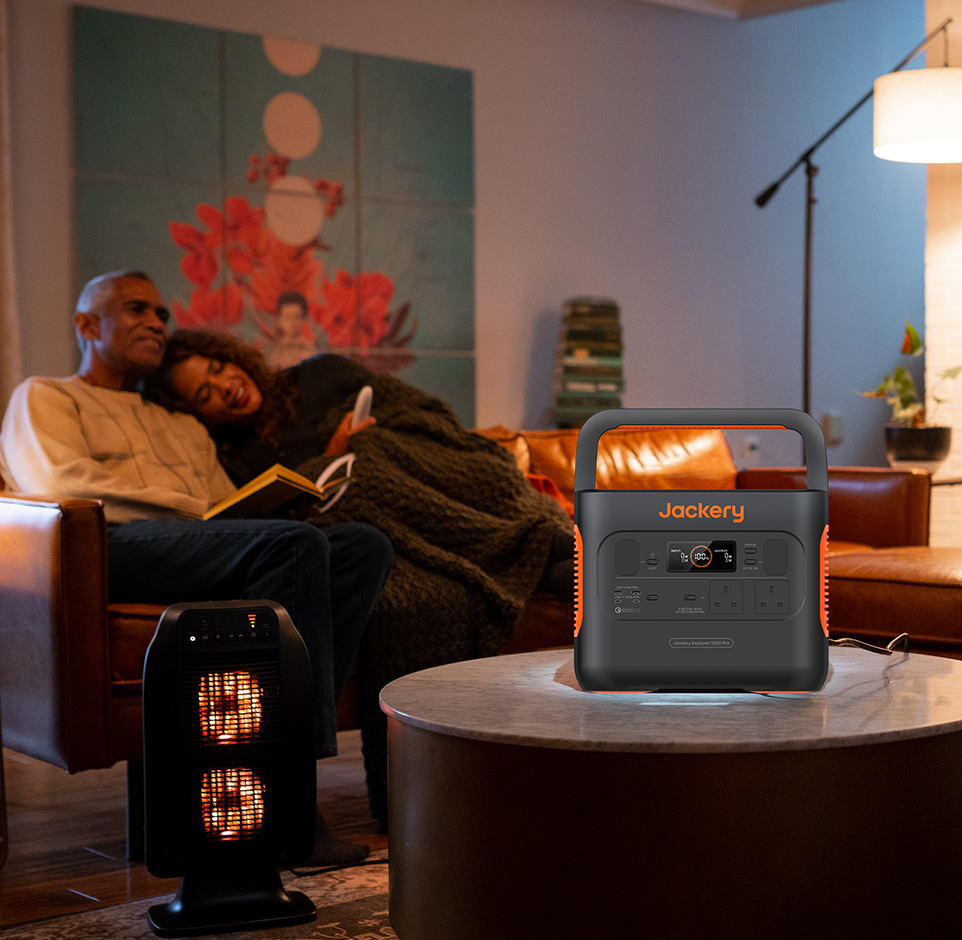
Jackery Explorer 1000 v2
The Jackery Explorer 1000 v2 is an excellent choice for powering a home TV and entertainment system, particularly as a seamless backup or portable power solution.

Seamless Protection with UPS Functionality: The most critical feature for home electronics is the built-in Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS). In the event of a power outage, the Explorer 1000 v2 engages its battery backup within 20 milliseconds. This instantaneous switch ensures your TV, streaming box, or gaming console does not flicker, reboot, or shut off, safeguarding your equipment and preventing data loss or interruptions to your viewing.
Quiet, Clean Indoor Operation: Unlike a noisy, fume-emitting gas generator, the Jackery Explorer 1000 v2 is designed for indoor use. It operates at a library-quiet level of less than 30 dB, allowing you to enjoy your movie or game without the distraction of generator noise. It produces no toxic fumes, making it perfectly safe to run inside your home or apartment.
Ample Power for Extended Viewing: The power station's capacity and output are perfectly matched for typical home entertainment needs. With a large 1070 Wh (Watt-hour) battery capacity, the Jackery can power a standard modern 50-inch LED TV (which typically consumes about 70–100W) for approximately 5-6 hours. This is enough time to watch several movies or a whole series of your favourite shows during a blackout.
The unit offers a 1500W continuous AC output (3000W peak), which is more than enough to power your TV, a soundbar, a streaming device, and a game console simultaneously.
Advanced Battery Safety and Lifespan: The v2 model features upgraded battery technology, making it a long-term investment for your home. It uses safer, more durable Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) battery cells. This chemistry is rated for over 4,000 charge cycles before degrading to 70% capacity, meaning it is built to last for many years of reliable use as home backup.
Jackery Explorer 500 v2
The Jackery Explorer 500 v2 is an ideal choice for powering a TV, especially in a mobile setting like a caravan or camper van, because it perfectly balances capacity, portability, and power quality for standard entertainment devices.

Optimal Power for TVs: With a 500W continuous output, it easily powers a typical LED/LCD TV (which draws between 50W and 150W), a streaming stick, a Blu-ray player, or a soundbar. The 512Wh capacity provides several hours of viewing time. For example, a common 100W Smart TV could run for approximately 4 to 5 hours on a full charge, which is perfect for an evening of entertainment or a couple of movies.
Portability & Easy to Take: Weighing only about 12.5 lbs (5.7 kg), the 500 v2 is highly portable. It can be easily moved from the vehicle to a picnic table or into the home during a power outage. It is designed to be space-efficient, fitting neatly into the tight storage compartments of an RV or caravan without taking up valuable living space.
Pure Sine Wave Inverter for Sensitive Electronics: The 500 v2 features a Pure Sine Wave inverter. This produces a clean, stable electrical waveform, identical to what you get from a standard wall outlet. This clean power protects sensitive electronics, ensuring your TV, game console, or router runs efficiently without the risk of damage or performance issues that can occur with modified sine wave inverters.
LiFePO4 Battery for Reliability and Longevity: It uses a high-grade LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) battery rated for 6,000 charge cycles to 70% capacity. This ensures years of reliable use for your road trips and home backups.
FAQs
The following are the frequently asked questions about the power consumption of TVs:
1. Will a 300-watt generator run a TV?
A 300-watt generator can power ceiling fans, lights, phone and laptop chargers, televisions, and small refrigerators. While not enough to power a whole house, it is handy during blackouts and for off-grid activities like camping.
2. How many watts does a 55-inch TV use per hour?
In general, a 55-inch LCD television requires approximately 180 watts, whereas an LED television requires approximately 80 watts.
3. How much does it cost to run a TV for 24 hours?
Running a modern TV for 24 hours costs between 12p and £1.30, based on an average UK electricity rate of around 25.73p per kWh and a power consumption of 50W to 200W. The actual cost is determined by the TV's wattage (which varies by model and age) and local electricity rates.
4. Is it safe to run a TV off a generator?
Technically, sure. However, doing so without protection is analogous to riding a motorcycle without a helmet—possible but unwise. Without a surge protector, your television is vulnerable to voltage spikes. These can occur when the generator begins, pauses, or struggles with unexpected variations in power demand.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how many watts a TV consumes helps you make better energy decisions at home. The power draw of each type, from modest 24-inch LEDs to big 70-inch OLEDs, has an impact on your electricity bills and overall energy footprint. You can dramatically reduce energy consumption by lowering brightness, selecting green settings, and turning off unnecessary televisions.
Before making a purchase, check the energy ratings to ensure you invest in efficient technology that saves both money and resources. Whether you power your TV with the mains, a generator, or a portable power station, conserving energy benefits both your household and the environment.