Over the past two decades, the maker movement has transformed from a niche hobbyist culture into a global phenomenon. Rooted in the do-it-yourself (DIY) ethos, this movement emphasises hands-on creation, innovation, and the democratisation of technology.
It leads to the rise of maker spaces. By fostering an environment of collaboration and innovation, maker spaces empower individuals to turn their ideas into tangible creations.
What is Maker Space?
Maker space, also known as hackerspace or fab lab, serves as a community hub where people can learn new skills, share knowledge, and work on projects collectively. It has several key characters:
1. Access to Core Tools and Equipment
While each maker space may have its own focus or speciality, they all provide the tools and environment necessary for turning ideas into physical reality. You might find 3D printers, laser cutters, CNC machines, soldering stations, and computers loaded with design software. At the same time, they often provide power for woodworking, metalworking, or crafting. This blend of old and new encourages creative thinking and cross-disciplinary experimentation.
2. A Wealth of Learning Resources
At maker space, you can focus on education and skill enhancement. Many offer workshops, classes, or mentorship programs to help beginners get started and give experienced makers new challenges to tackle. Wanna learn to code a microcontroller or try your hand at vinyl cutting? Resources at creator spaces are usually close at hand.
3. Open Collaboration and Community
Maker spaces thrive on collaboration. They’re designed not just as work areas but as communities where people with different skills and interests can share knowledge, solve problems together, and support each other’s projects. The open, inclusive maker studio atmosphere is key to fostering innovation and making sure everyone—from hobbyists to professionals—feels welcome.
 (Copyright Photo from: https://www.freepik.com/free-photo/young-children-making-diy-project-from-upcycled-materials_25810866.htm)
(Copyright Photo from: https://www.freepik.com/free-photo/young-children-making-diy-project-from-upcycled-materials_25810866.htm)
Common Types of Maker Spaces
Maker spaces can be found in a wide variety of settings, each tailored to meet the needs of its users:
1. School-Based Maker Spaces
Many schools and universities have adopted maker spaces to promote STEM and project-based learning. These spaces allow students to engage with hands-on technology and develop problem-solving skills in a creative environment.
2. Public Library Maker Spaces
Increasingly, public libraries are setting up maker spaces as part of their community services. These creator spaces are usually free to use and open to all, making them a great entry point for people who are curious about making but don’t have their own tools or workspace.
3. Private Innovation Labs and Co-Making Studios
Some maker spaces are run by private companies, startups, or coworking facilities. These may focus on entrepreneurship, product development, or industrial design and often cater to professionals or advanced hobbyists. They typically offer more advanced tools and business resources, sometimes requiring memberships or fees.
4. Home-Based or Personal Maker Spaces
For passionate hobbyists or independent creators, a home-based maker space can be the ultimate creative zone. These personal setups often include tools like 3D printers, soldering irons, or basic woodworking gear—tailored to the maker’s specific interests. While convenience and freedom to allow creators to tinker anytime inspiration strikes, home-based maker space should care about the electric power supply issues. You need to figure out if there is any power overload or any short circuit. It is important, especially for those who are considering building their own mini maker space in garages, basements, or spare rooms.
 (Copyright Photo from: https://www.freepik.com/free-photo/group-teens-doing-experiments-robotics-laboratory-boys-girls-protective-vr_59524775.htm)
(Copyright Photo from: https://www.freepik.com/free-photo/group-teens-doing-experiments-robotics-laboratory-boys-girls-protective-vr_59524775.htm)
Who Uses Maker Spaces?
As mentioned in the scenarios above, you can guess the major groups who love to go to maker space.
Far from being limited to engineers or tech experts, maker spaces are used by a diverse mix of creators who each bring their own goals and perspectives:
1. Hobbyists and Tinkerers
For hobbyists, maker spaces are like playgrounds for creativity. These are the folks who love to explore, build, and improve things just for the joy of it. From DIY drones to handcrafted furniture, maker spaces give hobbyists access to tools they might not have at home—and a supportive environment to work in.
2. Students and Young Learners
In educational settings, maker spaces help students move beyond textbooks by turning theory into practice. They offer a more engaging, hands-on way to explore STEM (and STEAM) subjects—encouraging critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity. For many young learners, a maker space is where schoolwork becomes a real-world experience.
3. Entrepreneurs and Startups
For entrepreneurs and product developers, maker spaces are valuable innovation hubs. They offer a low-cost way to create early prototypes, test ideas, and iterate quickly—without needing to invest in expensive equipment upfront. Some maker spaces even support business development through mentorship or networking opportunities.
4. Engineers and Designers
Even experienced professionals use maker spaces to explore ideas outside their regular job roles. Engineers might build passion projects or test experimental designs, while designers can prototype physical products or test out materials in a hands-on way. The flexibility and range of tools often spark new insights that might not emerge in a typical work environment.
5. Educators and Mentors
Teachers, librarians, and community educators are increasingly involved in maker spaces as facilitators or guides. They use these environments to create engaging learning experiences, run workshops, or support after-school programs. Many also benefit from the collaborative atmosphere, where sharing ideas and learning from others is part of the culture.
 (Copyright Photo from: https://www.freepik.com/free-photo/designers-team-working-3d-model_25182420.htm)
(Copyright Photo from: https://www.freepik.com/free-photo/designers-team-working-3d-model_25182420.htm)
How to Make Your Innovation in Maker Space Responsibly?
As more people turn to maker spaces for learning, innovation, and creative expression, there’s also a growing awareness of the broader impact these maker studios can have, which is, in particular, sustainability. the question naturally arises:
A Shift Towards Greener Making
How can we keep this innovation going without compromising our planet’s future? While maker spaces are designed to foster creativity and progress, they also consume energy and materials. Tools like 3D printers, laser cutters, and CNC machines can be energy-intensive, and waste from failed prints or disposable components can add up quickly.
In response, maker spaces are beginning to adopt more sustainable practices. The Remakery, located in South London, exemplifies sustainable innovation in a maker space. Established in a repurposed car park, this cooperative workshop focuses on reusing surplus materials and fostering a culture of repair and creativity. And they also offer workshops and events that teach participants how to transform waste into functional items to create a more sustainable environment.
Other than Remakery, more and more maker spaces are making an effort towards sustainability. Generally, they are embracing sustainable practices like:
- Encouraging the use of recycled or biodegradable materials
- Providing guidance on reducing waste and designing for durability
- Repairing or repurposing old tools and electronics rather than discarding them
- Supporting local sourcing and material reuse initiatives
 (Copyright Photo from: https://www.freepik.com/free-photo/bulb-with-3d-windmill-project-saving-energy_13328756.htm)
(Copyright Photo from: https://www.freepik.com/free-photo/bulb-with-3d-windmill-project-saving-energy_13328756.htm)
Integrating Green Technology
Beyond material reuse, some maker spaces are exploring renewable energy sources to power their operations.
- As the UK's longest-running free media lab, Access Space promotes sustainability by reusing technology and offering workshops that focus on creative reuse and digital arts.
- The Green Dragon Maker Space exemplifies sustainable innovation in maker space by installing an entirely solar-powered setup. It offers a wide array of equipment and resources for various projects.
Advocating sustainability in maker space is an action to deliver responsible innovation. The utilisation of solar energy, for instance, provides a clean, renewable power supply for tools and equipment. These systems reduce reliance on non-renewable energy for providing a stable power supply; more importantly, they serve as educational tools for comprehending sustainability for everyone.
How to Evaluate the Viability of Utilising the Solar Energy in Maker Space?
If you're thinking about integrating solar energy into your maker space, one of the first things to decide is which type of solar setup makes the most sense. Whether building a large public innovation hub or setting up a private workspace at home, there are two main categories to consider: installed (on-grid) systems and portable (off-grid) systems. Each has its strengths and trade-offs depending on your budget, space, and energy goals.
Installed Solar Power Solutions (On-Grid or Hybrid)
Installed solar systems are permanently fixed, usually on the roof or nearby ground, and are typically connected to the local power grid (on-grid) or paired with a battery system (hybrid). This kind of setup is ideal for public maker spaces, school or library-based labs, and home workshops with steady, long-term power needs.
Pros
High power output: Can run multiple machines like 3D printers, CNC routers, and laser cutters without worry.
Long-term savings: Reduces electricity bills significantly over time.
Grid connection: Ensures consistent power even on cloudy days or at night (if on-grid or hybrid).
Can feed energy back to the grid: Some systems allow you to sell surplus energy back.
Cons
High initial cost: Requires professional installation and infrastructure.
Permanent: Not suitable for mobile setups or spaces without ownership rights.
Permit and regulations: In some areas, installation may require permits, inspections, and planning, depending on your region.

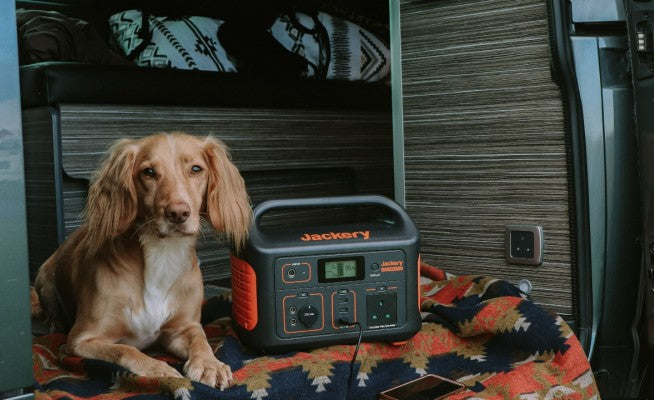
Portable Solar Power Solutions (Off-Grid)
A portable power supply or a portable solar generator—usually a combination of foldable panels and battery-powered generators—is an excellent choice for home-based maker spaces, pop-up events, mobile maker labs, or any situation where you don't have fixed infrastructure.
Pros
Take it anywhere: Suitable for both indoor and outdoor maker activities—on-site prototyping, remote workshops, or open-air demos.
Affordable: Lower upfront costs compared to fixed installations.
Plug-and-play: No need for installation—just set up the panel and start charging.
No grid needed: Useful in places where grid access is limited or unavailable.
Cons
Limited capacity: Not ideal for running high-power tools continuously.
Frequent monitoring: You’ll need to manage charging and consumption carefully.
Choosing What Works for You
Here's a quick guide to help you decide:
|
Consideration |
Go with Installed (On-Grid) |
Go with Portable (Off-Grid) |
|
Powering Heavy Equipment |
Yes |
Not Ideal for Large Tools |
|
Space Ownership |
Permanent building |
Flexible or Temporary Spaces |
|
Budget |
Higher Upfront |
More Affordable |
|
Mobility |
Fixed Setup |
Easy to Relocate |
|
Events/Workshops |
Requires Setup Location |
Perfect for Mobile Setups |
In short, an installed solar system might be worth the investment for a community or commercial maker space with a stable infrastructure. But if you are just getting started, experimenting at home, or need flexibility, a portable off-grid solar generator can offer freedom and sustainability without the hassle.
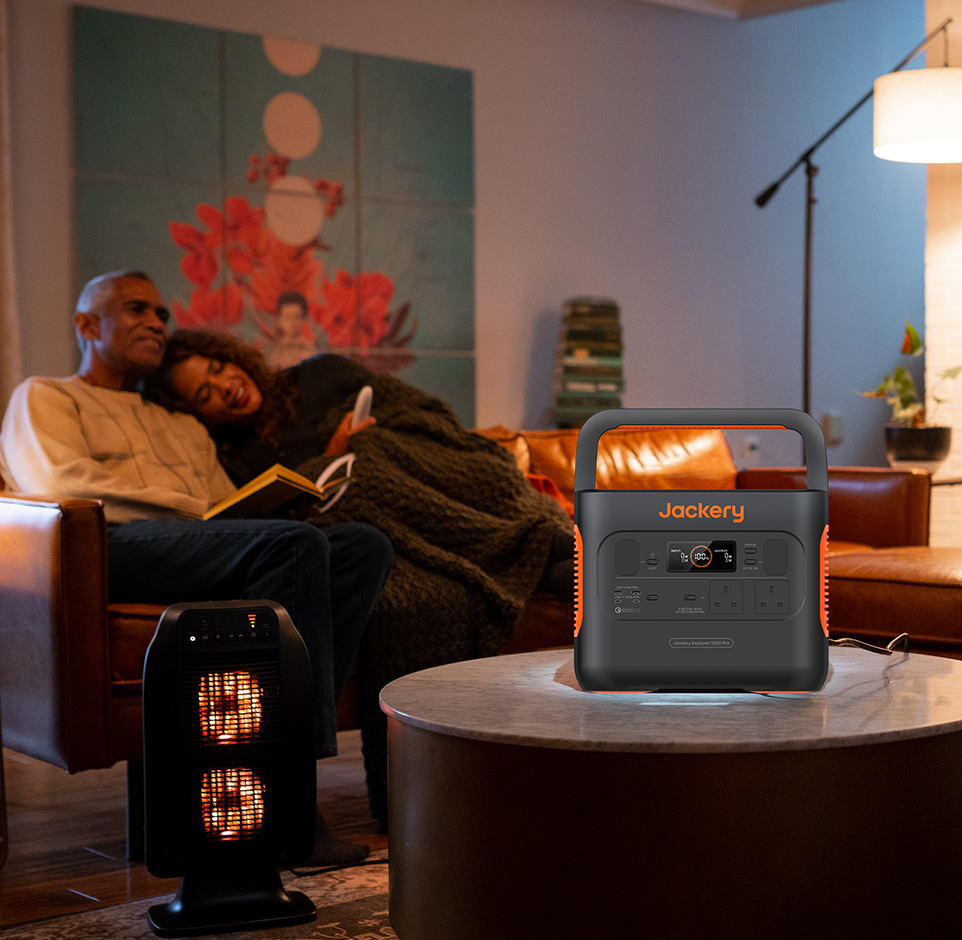
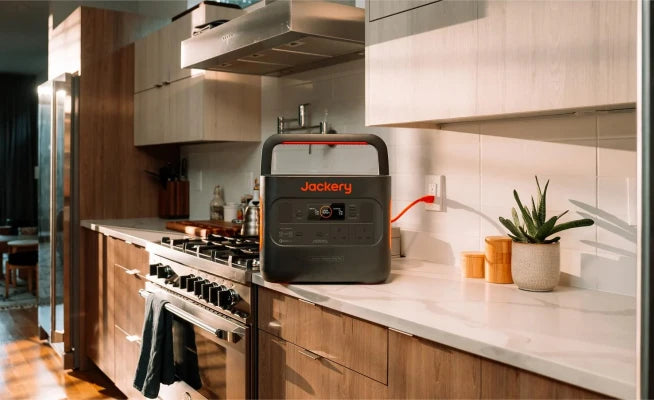
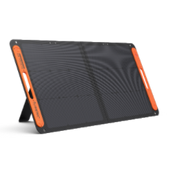
Introducing Jackery Solar Generator 2000 v2 for Maker Spaces
If you're considering a portable solar solution for your maker space—especially one that can keep up with the demands of real tools and equipment—the Jackery Solar Generator 2000 v2 is worth a closer look. It's designed not just for camping or backup power but also for serious creative work—both indoors and out.

Large Battery Capacity, Higher Power Supply
This all-in-one off-grid power station comes with a massive 2042Wh capacity and 2200W output, which means it can power many crafting tools like drills, grinders, saws, and more—all without needing a wall socket. Whether you're running a small bench setup in your garage or hosting a workshop in a park, this unit delivers stable and clean power.
Built to Last—And Built for Safety
One of the standout features of the Jackery Solar Generator 2000 v2 is its impressive 10-year lifespan, thanks to its 4,000+ battery life cycles. That makes it not just a short-term solution but a long-term investment in sustainable making.
Plus, it also features ChargeShield™ 2.0 Protection Technology, offering 62 layers of safety protection and full certification for international safety standards. That means you can use it around students, beginners, or sensitive electronics with greater peace of mind.

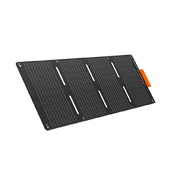
Efficient and Fast Charging with Jackery SolarSaga Panels
The package includes a Jackery SolarSaga 200W Solar Panel, which uses advanced multi-layer technology to reach up to 25% solar conversion efficiency. This ensures your generator charges faster and more reliably. And, this panel is foldable and easy to carry, so you can recharge the power station anywhere you go, whether it's a backyard shed or an off-grid retreat.

Backup Ready with UPS Functionality
The Jackery Solar Generator 2000 v2 isn’t just for sunny days. In the event of a power outage, it offers UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) capability. That means it can switch power sources in under 20 milliseconds, keeping your tools or electronics running without disruption—an especially valuable feature for digital fabrication equipment or in-progress projects.
Conclusion
Maker spaces are incredible hubs for creativity, learning, and innovation—and powering them responsibly is becoming more important than ever. Whether you’re running a community workshop, a school lab, or your own home maker studio, understanding the different solar energy options can help you make your things smartly, sustainably and responsibly.
Installed solar systems offer reliable, long-term power for larger setups, while portable solutions like this solar portable power station with solar panel complete set, Jackery Solar Generator 2000 v2 provide flexibility, mobility, and clean energy for makers on the go. If you are interested, please visit Jackery’s official website to learn more.
Reference
[1] Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maker_culture
[2] Available at: https://interreg-baltic.eu/project-posts/exploring-makerspaces-and-the-maker-movement/
[3] Available at: https://www.remakery.org/about/
[4] Available at: https://radicalbakers.org/green-dragon-maker-space