Homeowners can use solar power, battery storage, and other energy solutions to manage consumption and lower utility costs. As you explore these systems, you will encounter key terms for measuring power, such as watts (W) and megawatts (MW). One watt equals the energy transferred through a circuit in one joule per second.
A megawatt, on the other hand, refers to the amount of energy that travels through a circuit in 1,000,000 joules per second. So, how many watts are in a megawatt? One megawatt is 1,000,000 watts. A megawatt of electricity can power around 2,000 houses for around an hour.
|
Key Takeaways: |
|
What Is a Megawatt?
The term "megawatt" refers to the rate of energy conversion or consumption per unit of time. In other words, if a gadget has a power output of 1 megawatt, it can consume or generate 1 million joules of energy per second.
To better understand the concept of a megawatt, consider some everyday parallels. For example, a household air conditioner has a power output of about 1.5 kilowatts; therefore, 1 megawatt is equivalent to about 667 air conditioners running simultaneously.
Applications of Megawatts
Megawatts measure the power capacity of medium- or large-scale power plants, mainly used in:
Power Station Size: A medium-sized thermal power station may have an installed capacity of 500 megawatts.
Renewable Energy Projects: A large wind farm might include dozens of turbines with a combined capacity reaching hundreds of megawatts.
Industrial Electricity: The power consumption of large factories, steel mills, or data centres is often measured in megawatts. For example, a large data center may consume 10 to 50 megawatts.

What Is the Difference between a Megawatt and a Megawatt-Hour?
Megawatts (MW) measure instantaneous power. Megawatt-hours (MWh) measure total energy delivered in one hour. Example: A 5 MW solar plant running for an hour produces 5 MWh.
Think of a solar system as a water pipe: megawatts (MW) are the pipe's diameter, while megawatt-hours (MWh) are the water that flows through it in an hour.
What Is a Watt?
A watt (W) is the rate of energy used per second; 1 watt equals 1 joule per second.
Consider watts as an energy speedometer. A 10-watt light bulb uses 10 joules of energy per second to produce light (1 watt = 1 joule/second). Higher wattage means more energy is used over time.
Applications of Watt
Watts are used to rate energy use and equipment output.
Household Appliances: The power rating (in watts) of almost all electrical devices, including LED lights (20 W) and electric fans (100 W), appears on their nameplates.
Power Systems and Energy Engineering: In power generation, transmission, and distribution systems, the watt is used to describe the installed capacity of generator sets. For example, a household solar panel has a power rating of approximately 300–400 W.

What Is the Difference between a Watt and a Watt-Hour?
The terms "watt" and "watt-hour" refer to different concepts. Watts measure the rate of energy conversion, while watt-hours measure the total energy consumed or produced over time. For example, a 1000-watt electric furnace uses 1000 joules of energy per second. If it runs for an hour, it consumes one kilowatt-hour.
How Many Watts Are in a Megawatt?
In the domains of electricity, energy, and engineering, power unit conversion is fundamental and critical information. The conversion from "megawatt" (MW) to "watt" (W) is especially popular. So, how many watts is one megawatt? The following analysis clarifies this:
1 megawatt (MW) equals 1,000,000 watts (W).
This is the standard conversion relationship for the International System of Units (SI). "Mega" is a prefix meaning "million" (10⁶). One megawatt equals 10⁶ watts, or 1,000,000 watts.
This conversion relationship is constant and applies to the conversion of all power units.
For example: 2 megawatts equals 2,000,000 watts; 0.5 megawatts equals 500,000 watts, and so on. Furthermore, we may take this a step further by translating 1 megawatt to kilowatts, then to watts. As seen below:
One megawatt equals 1,000 kilowatts (kW).
1 kilowatt equals 1,000 watts.
Therefore, 1 megawatt equals 1,000 x 1,000 = 1,000,000 watts.
For your convenience, a table is provided below that converts various megawatt measurements to watts.
|
Megawatt [MW] |
Watt [W] |
|
0.000001 MW |
1 W |
|
0.000002 MW |
2 W |
|
0.000003 MW |
3 W |
|
0.000004 MW |
4 W |
|
0.000005 MW |
5 W |
|
0.000006 MW |
6 W |
|
0.000007 MW |
7 W |
|
0.000008 MW |
8 W |
|
0.000009 MW |
9 W |
|
0.0000001 MW |
0.1 W |
|
0.000001 MW |
1 W |
|
0.00001 MW |
10 W |
|
0.0001 MW |
100 W |
|
0.001 MW |
1,000 W |
|
0.01 MW |
10,000 W |
|
0.1 MW |
100,000 W |
|
1 MW |
1,000,000 W |
How to Convert Megawatts to Watts?
To convert megawatts (MW) to watts (W), or watts to megawatts, perform these three simple steps:
Step 1: Define the Original Value and Unit
Determine the value you wish to convert and its current unit. For instance, "750,000 watts" or "2.5 megawatts".
Step 2: Apply the Conversion Factor
To convert megawatts to watts, multiply by 1,000,000. The formulations are as follows:
Watts are calculated by multiplying Megawatts by 1,000,000.
Example 1: Converting 3 megawatts to watts yields 3,000,000 watts (3 x 1,000,000 = 3,000,000). To convert watts to megawatts, divide by 1,000,000. The formula goes as follows:
A megawatt equals 1,000,000 watts.
Example 2: Converting 500,000 watts to megawatts yields 0.5 MW (500,000 ÷ 1,000,000 = 0.5).
Step 3: Check the Results and Units
Check calculation accuracy and unit labels to avoid magnitude errors. You may also verify results with an online calculator (e.g., UnitConverters.net), but use these tools cautiously as they may not be completely accurate.

How Many Solar Panels Are Needed to Achieve a 1 Megawatt of Generating Capacity?
To create one megawatt (MW) of solar power, around 2,000 to 2,900 solar panels are required. This is highly dependent on the power output of the panels used. However, the quantity of solar panels required is determined by their power production, efficiency, and the amount of sunlight received at the site.
The greater the electricity production of the solar panels, the fewer panels are required. The specific figures are as follows:
|
Panel Wattage |
Approximate Panels Required for 1 MW |
|
350W |
~2,857 panels |
|
400W |
~2,500 panels |
|
450W |
~2,222 panels |
|
500W |
~2,000 panels |
(Source: eerenewables)
The type of solar panel matters. Monocrystalline silicon panels are more efficient. Fluctuations in UK sun irradiation directly affect a 1 MW plant's output.
Devon, Cornwall, and the south coast produce 1,100 to 1,200 kWh per square metre per year, whilst the Northeast, Scotland, and Northern Ireland may produce only 850 to 950 kWh per square metre per year. This suggests that a 1 MW system in Bristol may produce more than 25% more electricity annually than a similar system in Newcastle.
How Much Space Is Required to Establish a 1 Megawatt Solar Power System?
A 1 MW solar photovoltaic system requires a significant amount of space, at least 4,000-9,000 square meters. To maximise energy per square metre, rooftop panels are closely placed, either in an east-west orientation or with a tilted support system. A 1 MW rooftop solar system typically requires 4,000 to 5,000 square meters of headroom.
Ground-mounted solar farms require more acreage than rooftop solar farms, due to shading, tilting, and maintenance access. As a result, a fixed-tilt, south-facing 1 MW ground-mounted solar farm typically requires 6,000 to 9,000 square meters (1.5 to 2.2 acres) of space.
How Is 1 Megawatt-Hour of Electricity Stored?
Storing 1 megawatt-hour (MWh) of electricity typically requires a large battery energy storage device. A 1 MWh battery energy storage system (BESS) stores 1 megawatt-hour of electrical energy.
Components of a 1 MWh Battery Energy Storage System
A 1 MWh battery energy storage system has the following components:
Battery: The battery is the central component of the energy storage system (BESS), and it stores electrical energy. Energy storage systems can use a variety of batteries, such as lithium-ion batteries, lead-acid batteries, flow batteries, and so on.
The Power Conversion System (PCS): It converts the battery's direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), which can then be used by the power grid or other electrical equipment. The PCS also controls the power flow between the battery and the power grid or electrical equipment, as well as the battery's charging and discharging processes.
Battery Management System (BMS): It monitors and controls the performance of the battery, ensuring its safe and efficient operation.
Auxiliary Equipment: A 1 MWh Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) may incorporate cooling systems, fire suppression systems, and electrical enclosures in addition to the battery.

Advantages of a 1-MWh Battery Energy Storage System
A 1 MWh Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) can contribute to grid stability and reliability by providing grid support services such as frequency regulation and voltage support. Furthermore, it can reduce reliance on fossil fuels by storing excess energy from renewable sources and releasing it when needed.
How Many Homes Can 1 Megawatt-Hour of Electricity Power?
If we examine the average electricity consumption of a British household, one megawatt (MW) of electricity can power around 2,000 households for an hour. (Source: RatedPower) In the United Kingdom, an average home consumes approximately 10 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of energy every day. On a daily basis, 1 MWh (1000 kWh) can power approximately 100 houses for one day. However, this estimate is simply an average, and the actual number of households with electricity will vary greatly for a variety of reasons.
Factors Impacting the Number of Households Powered
The main factors influencing the number of households supplied with one megawatt hour of power are as follows:
Household Power Consumption Habits: power usage patterns differ greatly between British households. For example, families who use electric heating can consume more than 50% more power in the winter than those that use natural gas heating.
House Size: The number of family members in a household determines the total electricity use.
Building Insulation: Many British homes built in the twentieth century have poor insulation, resulting in higher heating costs in winter; homes that meet modern energy-efficiency standards can use 30%-50% less electricity than traditional homes.
Energy Pricing: High electricity prices encourage consumers to save energy and avoid needless consumption.

How Many Watt-Hours Does a Home Battery Need?
Home battery capacity is commonly measured in Wh. Most energy storage batteries have a capacity of 1000 to 13000 Wh, with bigger capacities typically costing more. Choosing the proper capacity for a home battery is not a matter of "bigger is better," but rather a scientific evaluation based on your household's energy use.
The number of bedrooms in your home determines the required solar panel capacity. To calculate the required battery capacity, first calculate your electricity consumption. Check your smart meter or monthly electricity bill to see your average usage.
Then divide by 30 to estimate your daily energy use, which will help you choose the appropriate battery size.
|
Property size |
Battery size (Wh) |
|
One bedroom |
2000 |
|
Two bedroom |
4000 |
|
Three bedroom |
8000 |
|
Four bedroom |
9500 |
(Source: theecoexperts)
According to the table above, if your daily electricity use is 8000 Wh (8 kWh), you will need a battery with a capacity of at least 8000 Wh to cover all your energy needs throughout the day. Remember, you are not constantly at home, so you might choose a smaller capacity battery.
In conclusion, for most British families, a battery size of 2000-4000 Wh is now the best feasible and cost-effective solution for boosting solar energy utilisation while providing dependable emergency support
However, if the goal is continuous off-grid operation, the battery capacity must be close to or exceed the typical daily electricity use, which is around 10 kWh (10,000 Wh).
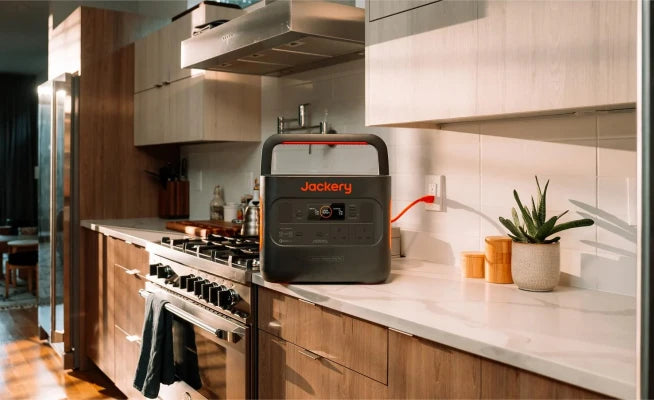
Jackery Portable Power Stations Explained
A unit like "megawatt-hour" (MWh) sounds distant, seemingly only for power plants or industrial settings. When we talk about home electricity, the real core unit is the watt-hour (Wh)—it determines our peace of mind during power outages, our ability to effectively store solar energy, and our ability to maintain normal life in emergencies.
Therefore, choosing a reliable and sufficient home energy storage battery becomes particularly important. Home energy storage isn't about having the biggest capacity; the key is finding the right balance, such as the Jackery Portable Power Stations.
The Jackery Explorer 3000 v2 and Explorer 2000 v2 models fall within the golden range of capacity—sufficient for emergencies and practical for daily use—making them a truly tailored solution for families.
Jackery Explorer 3000 v2 Portable Power Station
As a home energy storage battery system, the Jackery Explorer 3000 v2 has the following advantages:

Large Capacity, Power Freedom: The Jackery Explorer 3000 v2 boasts a 3072Wh energy reserve, meaning it can power a refrigerator for 1–2 days; charge a laptop more than 40 times; and keep home lighting running all night. It's an ideal energy storage station for home power outages, outdoor camping, and mobile offices.
Powerful Output, Fearless of High Load: The Jackery Explorer 3000 v2 delivers a maximum continuous output of 3600W, with a peak output of 7200W, easily handling high-power appliances such as air conditioners, electric kettles, and electric heaters. It uses pure sine wave inverter technology, ensuring stable output current and protecting delicate electronic equipment.
Fast Charging, Energy Self-Sufficient and Efficient: The Jackery Explorer 3000 v2 supports AC, solar, and vehicle charging. In AC charging mode, it can be fully charged in 1.8 hours. Its high solar input efficiency (maximum solar input power 1000W), combined with Jackery Solar Panels, enables a green cycle of generating electricity during the day and using it at night.
Safe and Reliable, Long-Life Design: The Jackery Explorer 3000 v2 uses a lithium iron phosphate (LFP) battery with a cycle life of over 4000 cycles (capacity retention ≥70%) and a lifespan of up to 10 years. Its built-in intelligent BMS system monitors temperature, voltage, and current in real time to ensure safe operation.
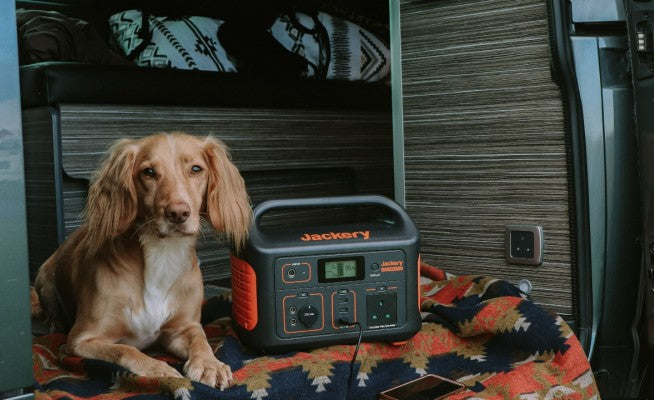
Jackery Explorer 2000 v2 Portable Power Station
As a home energy storage battery system, the Jackery Explorer 2000 v2 has the following advantages:

Practical Capacity, Suitable for Multiple Scenarios: The Jackery Explorer 2000 v2 is equipped with a 2042Wh capacity, sufficient for most households' basic power needs of 8–12 hours.
It provides reliable backup power during unexpected power outages, ensuring the continued operation of essential appliances, including refrigerators, lighting, and communication devices. In emergencies such as power outages, the power supply switches to a portable power source within 20 milliseconds.
Rich Interfaces, Multi-functional: The Jackery Explorer 2000 v2 features AC output (230V~50Hz), USB-A (maximum power 18W), and USB-C (USB-C1: maximum power 30W; USB-C2: maximum power 100W), allowing simultaneous charging of multiple devices such as mobile phones and laptops. It's especially suitable for family gatherings, nighttime lighting, children's studying, and remote work.
High Power Output, Worry-Free Emergency Use: The Jackery Explorer 2000 v2 has a maximum output of 2200W and a peak output of 4400W, capable of powering most household appliances, including lights (5W), refrigerators (15-520W), and electric kettles (800W). It can also support high-load devices such as electric ovens (1600W) and heaters (1800W), enhancing the family's ability to handle unexpected situations.
Fast Charging and Rapid Response: The Jackery Explorer 2000 v2 can be activated in emergency supercharge mode via a smart app. This power station can charge from 0% to 100% in just 1.33 hours, perfect for situations where you urgently need power. Even in regular AC charging mode, a full charge takes only 1.7 hours.
FAQs
The following are frequently asked questions about how many watts are in a megawatt.
1. What is 1 MW equal to?
A megawatt (MW) is a unit of power equal to 1,000,000 watts. Alternatively, 1 megawatt (MW) = 1,000 kilowatts (kW).
2. How much is 200 MW of power?
200 megawatts (MW) is 200,000,000 watts. It can also be converted to a more common unit: 200 megawatts equals 200,000 kilowatts. If it runs continuously for 1 hour, it will produce 200 megawatt-hours (MWh) of electricity, or 200,000 kWh. Simply put, 200 megawatts of electricity equals 200 million one-watt LED lights lighting up all of a megacity's streets at once.
3. How many homes would a MW of power?
If we examine the average British household's electricity consumption, one megawatt (MW) of electricity could power 2,000 dwellings for an hour. (Source: ratedpower)
4. How much is 500 MW?
A megawatt (MW) equals 1,000,000 watts (W); hence, 500 MW equals 500,000,000 W (500 x 1,000,000 watts = 500,000,000 W). This converts into 500,000 kilowatts (kW).
For example, a 500 MW generator running at maximum load for one hour would produce exactly 500 megawatt-hours (500,000 kWh) of electricity. This is equivalent to fast-charging 80,000 electric automobiles simultaneously (assuming 60 kilowatts per vehicle).
Final Thoughts
A megawatt (MW) is a unit of power equal to 1,000,000 watts. It is frequently used to determine the power output of large power plants, wind turbines, solar power plants, and other large power-producing equipment. Watt-hour (Wh) and megawatt-hour (MWh) are energy units that reflect the total amount of energy produced or consumed over a given time period.
For the average household, a megawatt-hour is a faraway idea, but household battery capacity is typically measured in watt-hours (Wh) and kilowatt-hours (kWh). For example, the Jackery Explorer 3000 v2 and Explorer 2000 v2 models provide the ideal battery capacity for both emergency and regular use.
References:
Ramos, H., Adrover, T., Coronado-Hernández, O., Perez-Sanchez, M., & Espina-Valdés, R. (2025). Optimization and Machine Learning in Modeling Approaches to Hybrid Energy Balance to Improve Ports’ Efficiency. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 5211.
Cotfas, P., & Cotfas, D. (2025). The Role of the Industrial IoT in Advancing Electric Vehicle Technology: A Review. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9290.