E-bikes are gradually becoming popular in the UK for daily commuting and leisure exploration. Whether riding to work, shopping, or just for fun, the number of people using e-bikes instead of cars steadily increases.
Although e-bikes sound attractive as an environmentally friendly and efficient mode of transportation, many people are worried about whether it will significantly increase electricity bills.
Therefore, some onlookers who have never owned an e-bike may wonder how much it costs to charge one. In the following content, we will explore the charging cost of e-bikes. Moreover, we recommend a method to charge an e-bike with lower costs: using a Jackery Portable Power Station. It can pair with Jackery Solar Panels to recharge with solar energy to save bills.
|
Key Takeaways: |
|
● The cost of charging an e-bike with a battery capacity of 600Wh is about 15p per charge. ● Replacing an e-bike battery usually costs between £200 and £800. ● The charging cost of an e-bike will be affected by charging frequency, electricity price, charger efficiency, ambient temperature, battery capacity, and battery health status. ● Storing cheap electricity with a portable battery energy storage system during off-peak hours to charge an e-bike when needed effectively reduces charging costs. ● Compared with traditional fuel vehicles, electric vehicles, and public transportation, e-bikes have significant advantages in terms of charging costs. ● Assuming that it is charged daily (from 0 to 100%) throughout the year (365 days), its charging cost is about 47 pounds. ● We highly recommend the Jackery Explorer 3000 v2 and the Explorer 2000 v2 as portable power supplies for charging your E-bike outdoors. They offer higher capacity and portability. |
How Much Does It Cost to Charge an E-Bike?
UK residents have become more cautious about household electricity consumption in recent years. Therefore, most users and potential buyers are concerned about how much it costs to charge an e-bike. Although we cannot provide completely accurate data, we can teach you how to estimate the charging cost of an e-bike.
Data Involved in Calculating the Cost of Charging an E-Bike
Calculating the cost of charging an e-bike is simple and mainly involves three data sets: e-bike battery capacity, electricity price, and charging frequency.
E-Bike Battery Capacity
Battery capacity is the basic parameter for calculating the cost of charging an e-bike, usually expressed in watt-hours (Wh) or kilowatt-hours (kWh).
A higher e-bike battery capacity means a more extended range and a slightly higher charging cost due to the larger amount of electricity required. Some standard e-bike battery capacities include 250Wh, 400Wh, 500Wh, and 750Wh.
Electricity Price
Calculating the cost of charging an e-bike requires understanding the price of electricity per kilowatt-hour. Check your recent electricity bill or contact your supplier to determine the electricity price per kilowatt-hour.
Charging Frequency
Charging frequency also determines the charging cost of an e-bike. If you need to ride your e-bike daily, it will consume more power and must be charged more frequently. But if you only ride it once a week, the charging frequency of an e-bike with the same battery capacity may be lower.
How Much Does It Cost to Charge an E-Bike?
Knowing the e-bike battery capacity, power price, and charging frequency will allow you to determine the charging cost. In the following section, we will go over how to calculate the cost of charging an e-bike. Please remember that the e-bike charging cost calculated in the following steps is simply an estimate and can only be used for reference.

Step 1: Convert E-Bike Battery Capacity to Kilowatt-Hours (kWh)
Most e-bike batteries have a capacity between 250Wh and 750Wh. Converting Wh to kWh only requires dividing the original data by 1000. For example, it takes 0.6 kWh to charge a typical 600Wh e-bike battery fully.
The capacity of some e-bike batteries may also be marked with voltage (V) and ampere-hour capacity (Ah). Then please convert the capacity of the e-bike battery into kilowatt-hours (kWh) according to the following formula:
Battery capacity (Wh) = voltage (V) x ampere-hour capacity (Ah)
Example: A common 48V, 10Ah e-bike battery has a capacity of 480 Wh (36V x 10Ah = 480 Wh).
Step 2: Calculate the Cost of a Single Charge for the E-Bike
According to step 1, the amount of electricity required to charge the e-bike is known, so multiply it by the electricity price used to calculate its single charge cost. According to the energy price cap announced by Ofgem from July 1 to September 30, 2025, the electricity cost per kilowatt-hour is 25.73 pence.
Example: The cost of a single charge of an e-bike that requires about 0.6kWh of electricity is about 15.44 pence (0.6kWh x 25.73 p/kWh ≈ 15.44p).
Step 3: Calculate the Charging Cost of an E-Bike Over some time
Once you have calculated the cost per charge of an e-bike, you can estimate the cost over time based on the number of charges.
Example: If you charge an e-bike with a battery capacity 600Wh three times a week, the charging cost is 46.32p (15.44p x 3 ≈ 46.32p).
The following are the charging costs of e-bikes with different battery capacities, for reference only:
|
Battery Capacity |
Single Charge Cost |
Charging Cost in a Week (Three Charges) |
|
250 Wh |
6.43p |
19.29p |
|
300 Wh |
7.72p |
23.16p |
|
350 Wh |
9.01p |
27.03p |
|
400 Wh |
10.29p |
30.87p |
|
450 Wh |
11.58p |
34.74p |
|
500 Wh |
12.87p |
38.61p |
|
550 Wh |
14.15p |
42.45p |
|
600 Wh |
15.44p |
46.32p |
|
650 Wh |
16.72p |
50.16p |
|
700 Wh |
18.01p |
54.03p |
|
750 Wh |
19.30p |
57.90p |
The above data is calculated based on an electricity price of 25.73p/kWh (energy price cap from July 1 to September 30, 2025) and is for reference only.
The Additional or Hidden Costs of Charging an E-Bike
E-bikes are a convenient and ecologically friendly mode of transportation and have a comparatively low charging cost. However, while individuals love the convenience of riding and the low price of electricity, they frequently neglect the additional or hidden expenditures associated with charging an e-bike.

Battery Replacement Costs
Most standard e-bike batteries on the market today are lithium batteries, and their service life is typically proportional to the number of charge and discharge cycles performed. In general, the cycle life of typical lithium batteries ranges between 500 and 1000 times.
You will incur significant costs when your battery capacity reduces dramatically and the range is insufficient to suit your needs. For riders, this may imply that the e-bike battery should be replaced every 3-5 years. Replacing an e-bike battery ranges from £200 to £800.
Charging Equipment Costs
E-bikes often come with a basic charger. However, if it is broken or destroyed, you may need to replace or buy an original e-bike charger. The cost of an e-bike charger ranges from £10 to more than £100, with the average price about £20.
If you need to move your e-bike from indoors to your garage or yard to charge it, you'll need to buy an outdoor extension wire. If you plan to charge your e-bike in a garage or indoors, you may need a fireproof, explosion-proof charging safety box.
Security Equipment Costs
Charging your e-bike poses a considerable danger of theft, particularly at public charging stations. As a result, you can invest in security measures to keep your e-bike from being stolen while charging. A strong e-bike lock, for example, can cost between £20 and £100. Alternatively, you may put a GPS tracker on your e-bike, which can track its location in real-time if stolen, costing between £50 and £150.
Insurance Costs
Charging a large battery regularly can be problematic if the house's electrical load capacity is limited. Furthermore, charging your e-bike exposes you to the risk of theft. E-bike insurance prices range from £5 to £15 per month. Bikmo, CycleGuard, and ETA provide comprehensive e-bike insurance policies to meet various demands and budgets.
What Factors Affect the Charging Cost of an E-Bike?
Charging costs, one of the core expenses of using e-bikes, are affected by many factors. The following will analyse the key factors that affect the charging costs of e-bikes.

Charging Frequency
If you commute long distances every day, often use high-assist mode or climb steep slopes, you need to charge more frequently, and the charging cost of e-bikes will be higher. On the contrary, flat roads can extend the battery life of e-bikes, thereby reducing the charging frequency and cost.
Electricity Price
The higher the electricity price per kilowatt-hour (kWh) you pay, the higher the charging cost of e-bikes. For charging the same e-bike battery with a capacity of 500Wh, someone using a unit electricity price of 20p/kWh will pay almost twice as much as someone using a unit electricity price of 10p/kWh.
Charger Efficiency
Almost no e-bike charger is 100% efficient because some energy is always dissipated during charging. High-efficiency chargers may reach 85%-90%, wasting less electricity. Old or low-quality chargers may be less efficient, at 70% -80 %, meaning you need to buy more power to charge the battery fully.
Ambient Temperature
Extreme temperatures can cause e-bike batteries to become inefficient, increasing the frequency and charging costs. For example, an e-bike's battery performance will decline in hot summer weather, forcing more frequent charging to maintain the desired range.
Battery Capacity
The larger the e-bike battery capacity, the more power it needs to charge each time fully and the higher the cost. For example, an e-bike battery with a capacity of 500Wh requires more power than an e-bike battery with a capacity of 300Wh, and the charging cost is naturally higher.
Battery Health
As the battery ages, its maximum capacity decreases, meaning the distance it can travel on a full charge becomes shorter. The e-bike must be charged more frequently to travel the same distance, increasing total power consumption and charging costs.
How to Reduce the Charging Cost of E-Bike?
Although the cost of charging an e-bike is already low, there are still ways to reduce it. E-bike users can reduce charging costs by optimising charging habits, switching to cheaper electricity, and using renewable energy.

Optimise Charging Habits
If it is more convenient, charge the e-bike as you use it rather than charging it completely every time. For example, recharging the battery after a short ride can increase battery life and lower the cost of a single charge.
Furthermore, charging is more efficient in regular indoor temperatures, requiring less electricity than at high temperatures, resulting in cheaper charging expenses. If you have a time-of-use power rate, avoid charging your e-bike during high electricity consumption times, such as on weekdays during the daytime.
Reduce Unnecessary Power Consumption
After charging, always unplug the charger and power outlet. Even while not in use, the charger uses very little electricity. Always turn off the e-bike's power when not in use to prevent unnecessary discharge. If the e-bike has separate switches for controlling auxiliary equipment like the display, turn them off when parked.
Find a Free Charging Point
If your workplace allows it, charge your e-bike in the office during working hours. Shopping malls, supermarkets, gyms, and other establishments may also offer free power outlets for clients. Please gently ask the store staff if you can charge your bike beforehand. You may also utilise charging service platforms like Zap-Map to locate free charging stations nearby.
Take Advantage of Time-of-Use Electricity Prices
If you utilise time-of-use electricity tariffs, such as Economy 7 or Economy 10, you can charge your e-bike during off-peak hours when electricity costs are lowest. A more straightforward and practical option is to use the e-bike's built-in timed charging feature or purchase a smart socket timer that will start automatically during off-peak hours.

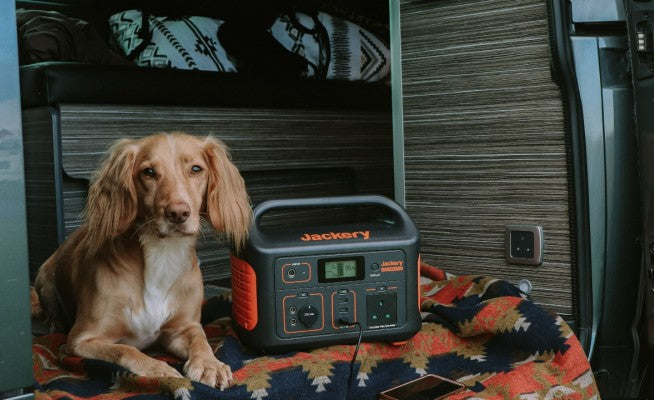
You can also utilise a portable battery energy storage device (such as the Jackery Explorer 3000 v2 or 2000 v2) to store low-cost electricity during off-peak hours and then charge your e-bike when necessary.
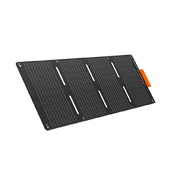
Take Advantage of Renewable Energy
If your living situation allows it, adding modest solar panels to power your e-bike can help you save money on charging or offset it. Although the initial expenditure on a solar system is expensive, it can balance the expense of charging your e-bike in the long run, particularly during sunny seasons. Equipping solar panels with energy storage batteries allows e-bikes to be charged for free even when the sun is not shining.
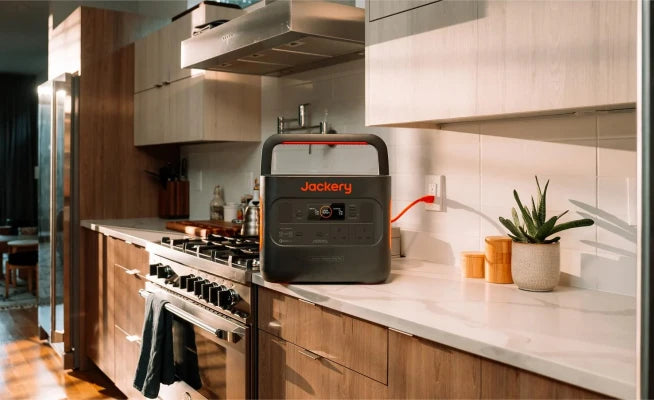
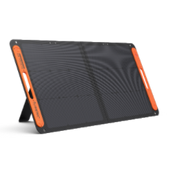
Jackery Portable Power Stations for E-Bikes
E-bikes give you incredible freedom to explore, but that freedom is limited by battery range. Jackery Portable Power Stations are designed to be relatively compact and lightweight (especially models like the Explorer 2000 v2), making them easy to transport in your car, RV, or even on a cargo bike. This allows you to charge your e-bike in remote locations, during camping trips, at trailheads, or anywhere a wall outlet isn't available.
E-bike chargers use standard AC wall power. Jackery power stations provide multiple AC outlets, meaning you plug your e-bike charger directly into the Jackery, just as you would at home. No special adapters or complex setups are needed.
Jackery offers a range of capacities (Wh), from smaller units suitable for a single top-up to larger ones that can fully recharge an e-bike battery multiple times (like the Explorer 2000 v2 or 3000 v2). This allows e-bike riders to pick a model that matches their typical ride length and charging needs.
How to Charge an Electric Bike by Jackery
Step 1: This is the fastest way. Plug the Jackery's AC charging cable into a standard household wall outlet. The 2000 v2 can go from 0% to 100% in a remarkable 1.7 hours (or even faster to 80% in 1.33 hours using "Emergency Super Charge Mode" via the app, if available for your model). Charge the Jackery Explorer 3000 v2 from the wall outlet (1.8 hours), carport (36 hours) and SolarSaga 200W solar panels (5.5 hours).
Step 2: Locate the standard AC (alternating current) outlets on the Jackery Explorer 2000 v2. It typically has multiple such outlets. Connect the AC charging brick and cable to your e-bike and plug it directly into one of Jackery's AC outlets.
Step 3: Plug the specialised connector end of your e-bike charger into the charging port on your e-bike. This port might be on the frame or directly on the removable battery.
Step 4: The Jackery's display will show the current power output (how many watts your e-bike charger is drawing) and the estimated remaining runtime of the Jackery.
Step5: Once your e-bike battery is fully charged, disconnect the charger from the e-bike and the Jackery.
Jackery Explorer 2000 v2
The Jackery Explorer 2000 v2 is another excellent choice for charging e-bikes. It offers a compelling balance of capacity, power, and portability. While the 3000 v2 offers even more, the 2000 v2 is often a "sweet spot" for many e-bike users.

Enough Power to Charge E-bikes: E-bike batteries typically range from 300Wh to 750Wh. With 2042Wh capacity, the Explorer 2000 v2 can fully recharge most e-bike batteries 2 to 4 times. For instance, Jackery states it can charge a 625Wh e-bike battery approximately 2.3 times. This is fantastic for multi-day trips or for charging multiple e-bikes.
High AC Output: E-bike chargers are relatively low-wattage devices (usually under 200W). The 2000 v2's high 2200W continuous output and 4400W surge means it can power any e-bike charger with ease and efficiency, providing stable power without straining the unit. This also leaves plenty of headroom for charging other devices simultaneously.
Enhanced Portability: Weighing around 17.5 kg (38.6 lbs), the Explorer 2000 v2 is notably lighter and more compact than the larger 3000 v2. This makes it significantly easier to transport in a vehicle, RV, or even a robust cargo e-bike trailer, striking a better balance between capacity and mobility for many users.
Fast and Flexible Recharging: The 2000 v2 can be recharged from a wall outlet in 1.7 hours, a massive advantage for quick turnarounds between rides. With up to 400W of solar input, you can recharge the unit in 5.5 hours of good sunlight, making it perfect for sustained off-grid adventures. This closes the loop for accurate renewable e-bike charging.
Jackery Explorer 3000 v2
The Jackery Explorer 3000 v2 is an ideal e-bike charging solution, especially for those who want maximum freedom and reliability.

Massive Capacity and Output: Most e-bike batteries range from 300Wh to 750Wh. With 3072Wh, the Explorer 3000 v2 can fully charge a 625Wh e-bike battery 3-4 times. This is perfect for extended multi-day trips, powering several e-bikes, or providing significant backup for unexpected detours. You'll rarely worry about running out of juice for your e-bike, even on ambitious tours.
E-bike chargers draw relatively little power (e.g., 50W to 150W). The 3000 v2's 3600W continuous output is overkill, which is good! The power station can easily handle your e-bike charger with plenty of overhead, ensuring stable and efficient charging without being strained. It can even power fast chargers if your e-bike uses one.
LiFePO4 Battery: It utilises a LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) battery, which is known for its excellent durability, long cycle life (up to 4000 cycles to 70%+ capacity), and enhanced safety compared to other lithium-ion chemistries. LiFePO4 is also known for its thermal stability and reduced risk compared to other lithium-ion types, which is crucial for a large power device.
Ultra-Compact and Lightweight: Despite its high capacity, the Explorer 3000 v2 is engineered to be notably smaller and lighter than previous models. Weighing around 59.52 lbs (27 kg), it's designed for easier portability, making it a dependable companion for e-bike adventures.
Off-Grid Freedom: Pairing the Explorer 3000 v2 with Jackery SolarSaga 200W solar panels transforms it into a full-fledged solar generator. This is invaluable for remote camping, overlanding, or long-distance e-bike touring with nonexistent wall outlets. You can ride all day, set up your solar panels to recharge the Jackery, and then use the Jackery to charge your e-bike overnight, creating a self-sustaining cycle.
Comparison of E-Bike Charging Costs with Alternative Transportation
After reading the above, you have all the information about how much it costs to charge an e-bike. The following will compare the charging cost of e-bikes with the cost of traditional cars, electric cars, and public transportation to provide a reference for different travel needs.
Fuel Cost of Traditional Cars
Traditional cars have higher fuel costs and are greatly affected by oil price fluctuations. According to Reightgoodbikes, in the UK, the annual fuel cost of a medium-use car is about £1,300.
Charging Cost of Electric Cars
Like e-bikes, electric cars' charging costs depend on their battery capacity and electricity prices. If your electric vehicle is equipped with a 50kWh battery, based on the energy price cap in the third quarter of 2025 (25.73p/kWh), it will cost about 1286.5p (£12.87) to fully charge.
In the UK, electric cars are usually charged through public charging stations, which are more expensive. Here are the charging standards of several electric vehicle charging stations in the UK:
|
Electric Car Charging Points |
Ionity |
Instavolt |
Osprey |
BP Pulse |
|
Charge Per kWh |
£0.74 |
£0.85 |
£0.82 |
£0.44-0.85 |
|
50 kWh of Charge |
£37 |
£42.5 |
£41 |
£22-42.5 |
|
100 kWh of Charge |
£74 |
£85 |
£82 |
£44-85 |
(Data Source: Carwow)
Public Transportation Costs
In the UK, the cost of public transportation such as buses, subways, trams, and trains is mainly fixed fares, which are suitable for frequent, long-distance or cross-regional travel. Regardless of the type of public transportation, the price depends on the city, route, ticket type, payment method, and distance. Here are the costs of several public transportation methods in the UK:
|
Transport Mode |
Estimated Monthly Cost (£) |
Annual Cost (£) |
|
Bus (London) |
£100 |
£1200 |
|
Bus (Outside London) |
£120 |
£1440 |
|
Bus (Manchester) |
£80 |
£960 |
|
Tram (Manchester) |
£50 |
£600 |
|
Tram (Sheffield) |
£60 |
£720 |
|
London Underground |
£300 |
£3600 |
|
National Rail |
£600+ |
£7200+ |
(Data Source: Reightgoodbikes)
E-bike Charging Costs
In the UK, an ordinary e-bike's battery capacity is about 0.5kWh. According to the energy price cap (25.73p/kWh) announced by Ofgem in the third quarter of 2025, the charging cost of an e-bike with a battery capacity of 0.5kWh is 12.87 pence. Assuming that it is charged daily (from 0 to 100%) throughout the year (365 days), its charging cost is about 47 pounds.
Based on the foregoing, traditional fuel cars confront high oil prices and environmental concerns. Although electric vehicles are inexpensive at home, they require professional charging equipment. Public transit is a dependable choice for car-free groups, but its reach is restricted. In contrast, e-bikes provide significant cost savings and are environmentally friendly, making them ideal for short-distance riding.
FAQs
The following are frequently asked questions about the costs of charging an electric bike.
1. How much does it cost to charge my e-bike?
The exact cost of charging an e-bike depends on the battery's size and the electricity price in your area. If your e-bike has a 300Wh battery and the electricity price is 25p/kWh, a full charge will cost around 7.5p.
2. How much does it cost to charge an electric bike in the UK?
In the UK, charging an e-bike typically costs between 5p and 22p, depending on the electricity price and the battery's size. For example, a 500Wh battery will typically cost around 14p to fully charge (from 0% to 100%).
3. Does charging an e-bike use a lot of electricity?
No, charging an e-bike typically doesn't use much electricity. Some standard e-bike battery capacities include 250Wh, 400Wh, 500Wh, and 750Wh, meaning charging only takes 0.25 to 0.75 kWh. Large household appliances such as dryers can run up to 1500kW, which means they consume about 1.5 kWh of electricity for one hour.
4. How often do I need to charge my e-bike?
Most e-bikes need to be charged every 1-2 days for daily commuting. However, how often you charge your e-bike depends on how usually you ride. For example, an e-bike with a 300Wh battery can typically travel 25km to 80km on a single charge with average use. An e-bike with a 400Wh battery can typically travel 40km to 100km on a single charge with average use.
Final Thoughts
Compared with traditional fuel vehicles, electric vehicles, and public transportation, e-bikes have significant advantages in terms of charging costs. Although it is difficult to calculate precisely how much it costs to charge an e-bike, as long as you know the e-bike battery capacity, electricity price and charging frequency, you can roughly estimate it. For example, the single charge cost of an e-bike with a battery capacity 600Wh is about 15 pence. Optimising charging habits can also effectively reduce the charging cost of e-bikes.